SAP MM (Materials Management) is a module of the SAP ERP software package from SAP AG that is used for Procurement Handling and Inventory Management. SAP Materials management covers all tasks within the supply chain, including consumption-based planning, planning, vendor evaluation and invoice verification.
Key Components of SAP Materials Management
MM – CBP (Utilization Based Arranging) …
MM – PUR (Buying) …
MM – SRV (Outer Administrations The board) …
MM – IV (Stock Administration) …
MM – IV (Operations Receipt Confirmation)
Benefits of Implementing SAP Materials Management
Improves generally speaking stock administration.
limits and wipes out stock misfortunes.
diminishes the time and work spent on keeping up with stock.
diminishes material wastage by trying not to stock on out of date or pointless items.
brings down work costs and streamlines work business.

Challenges and Solutions
- Inaccurate or partial Bill of Materials listing from the engineering firm.
- Engineering requisition issues.
- Purchase order revisions and inaccuracies.
- Shipping and receiving errors causing inaccurate inventory levels.
- Inaccurate material inventory counts.
- Inventory adjustments.
- etc.

Future Trends in SAP MM
The fate of SAP MM lies in its coordination with arising advances like man-made reasoning (computer based intelligence), AI (ML), and the Web of Things (IoT). By signing up for a complete SAP MM course, experts can acquire the information and abilities to really use these innovations.

How to Implement SAP Materials Management Successfully

Here are a few hints for effectively executing SAP Materials The board (MM):
Set up precise and steady expert information
Make a material expert
Characterize the different levels
Utilize unequivocal standards for material quality
Make shrewd determinations of suppliers
Utilize an expert as materials director
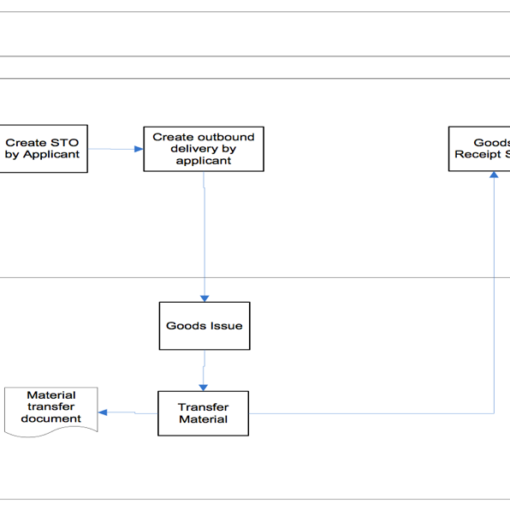
The acquirement cycle in SAP MM includes:
Recognizing the material required and reaching the suitable providers
Making a buy demand
Producing the buy request
Creating merchandise receipt
Creating the receipt
The SAP MM module has two significant expert information: material and seller. The most noticeable and broadly utilized parts are Expert Information, Buying, and Stock
What is the use of split valuation in SAP MM?
Real-world Examples
True models are stories, contextual investigations, tributes, or information that delineate how an item or administration has tackled an issue. They ought to be situated as a matter of fact and trigger feelings.
True models can be utilized in: Introductions, Showing supportability, Political overviews, Blended reality.
Here are a few instances of true models:
Involving separated inspecting for a political overview
GrowthPath Examination Connector for Dear Stock
PassGen/Send SMS – Custom secret word generator for numerous dialects
Japan Carriers utilizes a HoloLens to assist with preparing engineers without visiting a shelter
True models ought to incorporate important realities, details, and rates that back up the model. They can exhibit the intricacy and unconventionality of main problems, and can animate decisive reasoning.
Comparison with Other Supply Chain Management Systems
Compare Logistics and Supply Chain Management
While supply chain management handles activities between separate entities, logistics focuses on the internal movement of goods. Additionally, SCM supports all purchasing, production and distribution of goods. Logistics, meanwhile, moves and stores goods between different points in the supply chain.

Common Mistakes to Avoid in SAP MM Implementation
- Failing to Develop a Comprehensive Strategy. …
- Poor Project Scope Definition. …
- Insufficient Risk Management. …
- Inadequate Testing and Quality Assurance. …
- Ineffective Project Management and Team Collaboration. …
- Failure to Adapt to Changing Business Requirements.

FAQs
A. What is SAP Materials Management?
SAP Materials Management is an integral module within the SAP ERP system, focused on streamlining procurement processes, managing inventory, and optimizing material flow throughout the supply chain.
B. How does SAP MM improve procurement processes?
SAP MM enhances procurement processes by automating requisition creation, purchase order generation, and goods receipt, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
C. Can SAP MM be customized for specific industries?
Yes, SAP MM is highly customizable to meet the unique requirements of different industries, ensuring flexibility and adaptability.
D. Is SAP MM suitable for small businesses?
While SAP MM is robust, its implementation can be resource-intensive. Small businesses may explore scaled-down versions or cloud-based solutions for a more tailored approach.
E. What are the costs associated with SAP MM implementation?
The costs of SAP MM implementation vary based on factors like company size and customization requirements. Organizations should consider both initial and ongoing costs.
XIV. Conclusion
A. Recap of SAP Materials Management Importance
In conclusion, SAP Materials Management emerges as a game-changer in optimizing supply chain processes. Its comprehensive features contribute to cost efficiency, improved inventory control, and streamlined procurement.
B. Encouragement for Implementation
For organizations yet to explore the benefits of SAP MM, the time is now. The implementation may pose challenges, but the long-term rewards in terms of efficiency and competitiveness are well worth the investment.
You may be interested in:
is SAP Consultant a good career ?
Top SAP MM Consultant Interview Questions: Prepare for Success