What is SAP PLM?
SAP PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) is the process of managing a product’s lifecycle from inception, through design and manufacturing, to sales, services, and eventually retirement. It is the foundation for digital thread, ensuring supply chain agility and business continuity. Product lifecycle management enables firms to reduce costs, expedite time to market, and achieve the highest levels of quality and compliance by providing data governance and traceability.
As a technology, PLM software helps organizations to develop new products and bring them to market. The software makes it easy to track and share data along the product value chain, from initial design through manufacturing, supply chain management and operations, and asset maintenance.
Product lifecycle management software enables geographically-dispersed, multi-disciplinary, teams to strategically collaborate with partners and customers using trusted, up-to-date product information.

PLM Fundamentals
PLM plays a significant role in helping manufacturers produce the next generation of products at a reduced cost and with a faster time to market in an age when innovation is critical to corporate survival and success. While PLM can be viewed as a business strategy, three fundamentals have an impact on how teams function and an organization’s ability to grow and thrive:
- Universal, secure, managed access, and use of product definition information.
- Maintenance of the integrity of that product definition and related information throughout the life of the product.
- Management and maintenance of the business processes used to create, manage, disseminate, share, and use the information.
Phases of product development
There is no single industry standard when it comes to describing the stages of product development. The phases listed below, on the other hand, reflect a normal development cycle.
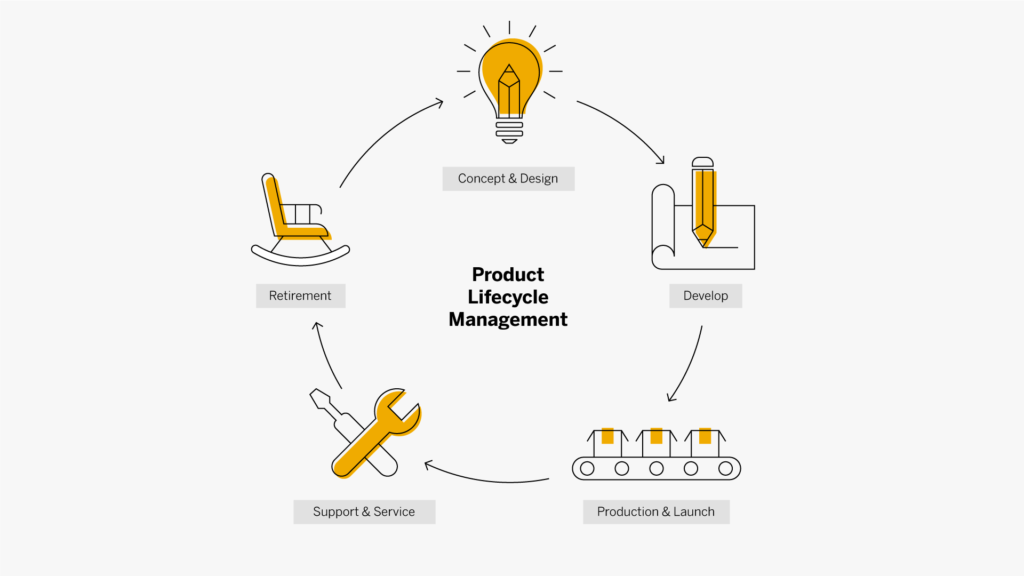
- Concept and design: The ideation phase, where a product’s requirements are based on criteria such as competitive analysis, market gaps, or consumer needs.
- Develop: The product’s detailed design, as well as any relevant design tools, will be created. Validation and analysis of the anticipated product, as well as prototype development and field testing, are all part of this step. This provides critical feedback on how the product is being utilized and what improvements are required.
- Production and launch: Feedback from the pilot is utilized to modify the design and other components in order to create a market-ready version. The new product’s production is ramped up, then launched and distributed to the market.
- Service and support: Following the launch of the new product, the period of time when service and support is offered.
- Retirement: The product’s withdrawal from the market, as well as any retrials or absorption into new concept ideas, must be managed towards the end of its lifecycle.
have you interested in SAP courses? then click here…
How does an SAP PLM system work?
A PLM system provides designers and engineers with real-time access to the crucial data they require. The system streamlines project management by connecting CAD (computer-aided design) data with a bill of materials and other enterprise data sources, such as integration with an ERP system, and manages this product data through all stages of the product development lifecycle.
PLM also keeps designers and engineers working in a vacuum by providing access to other sources of data such as customer and analyst feedback on current products, field performance data, and visibility into the limitations of downstream processes such as production.
Beyond design and engineering, a PLM system also helps teams. It can give business stakeholders and/or suppliers a “single source of truth” for easy feedback delivery early in the product development process.
Evolution
In the 1980s, American Motors Corporation (AMC) was a minor player in the automotive business. The company lacked the massive budgets of the market’s larger participants, limiting its ability to compete effectively. The initial iteration of product lifecycle management was conceived by AMC leadership, who wanted to track products from conception through end-of-life in order to optimize procedures and compete more effectively.
From concept to procurement and production, the information obtained was leveraged to make better decisions. By the mid-1990s, AMC had increased its market share and had been purchased by Chrysler, making it the auto industry’s lowest cost-maker.
PLM is now used throughout the manufacturing industry to promote cooperation, improve innovation, and efficiently support growth by designing to consumer demand.
Benefits of SAP PLM
Improved product quality: SAP PLM allows companies to design and test products more thoroughly, resulting in higher quality products that are more reliable and durable. The software also helps companies identify and address quality issues earlier in the product development process, which can save time and money.
Faster time to market: By streamlining product development processes, SAP PLM can help companies bring new products to market more quickly. This is especially important in industries with high levels of competition, where being first to market can give a company a significant advantage.
Increased efficiency: SAP PLM helps companies automate many of their product development processes, such as change management, document control, and bill of materials management. This reduces the time and effort required to complete these tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Better collaboration: SAP PLM allows teams to collaborate more effectively, even if they are located in different parts of the world. The software provides a single source of truth for all product data, making it easier for teams to work together and share information.
Cost savings: By improving product quality, reducing time to market, increasing efficiency, and facilitating better collaboration, SAP PLM can help companies save money. In addition, the software can help companies avoid costly mistakes by catching errors early in the product development process.
Regulatory compliance: SAP PLM helps companies stay in compliance with regulatory requirements, such as environmental regulations and safety standards. The software provides tools for managing product data and documentation, making it easier to track and report compliance-related issues.
Better customer satisfaction: SAP PLM helps companies create products that better meet customer needs and preferences. By improving product quality and reducing time to market, companies can more effectively compete in the marketplace and satisfy customer demand.
What is the difference between SAP and PLM?
the difference between SAP and PLM:
- SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing): SAP is a software company that offers a suite of enterprise software solutions to help organizations manage various aspects of their business operations. SAP’s flagship product is the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, which integrates different business functions such as finance, human resources, sales, procurement, inventory, and more into a single unified platform. SAP’s ERP system allows companies to streamline processes, access real-time data, improve decision-making, and enhance overall efficiency.
- PLM (Product Lifecycle Management): PLM, or Product Lifecycle Management, is a business approach and set of software solutions specifically focused on managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its initial concept to its retirement or disposal. PLM is mainly used in industries that involve extensive product development, such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, consumer goods, and electronics.
PLM software enables collaboration among various departments involved in product development, including engineering, design, manufacturing, marketing, and sales. It centralizes product data and documents, manages product changes, tracks revisions, and ensures regulatory compliance. The primary goals of PLM are to improve product quality, reduce time-to-market, optimize manufacturing processes, and enhance product innovation.
In summary:
- SAP is a software company that provides a suite of enterprise software solutions, including ERP, for managing various business functions across an organization.
- PLM is a strategic business approach and a set of software solutions focused specifically on managing the entire lifecycle of a product from conception to disposal in product-oriented industries.
While SAP offers an ERP system to manage diverse business functions, PLM is more specialized and concentrates specifically on product development and lifecycle management processes. In certain cases, organizations may integrate their PLM processes with SAP’s ERP system to streamline and manage their product-related information within their broader business operations managed by SAP.





