Understanding the Manufacturing Industry’s Challenges
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a digital revolution, driven by the need for increased efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. Traditional manufacturing processes are being disrupted by emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing. To stay ahead of the curve, manufacturers must adopt innovative solutions that can streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and enhance decision-making.
SAP, a leading provider of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, has emerged as a critical tool for manufacturers to address these challenges and drive transformation. By leveraging SAP’s comprehensive suite of solutions, manufacturers can gain a competitive edge, improve operational excellence, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
The Role of SAP in Manufacturing Transformation
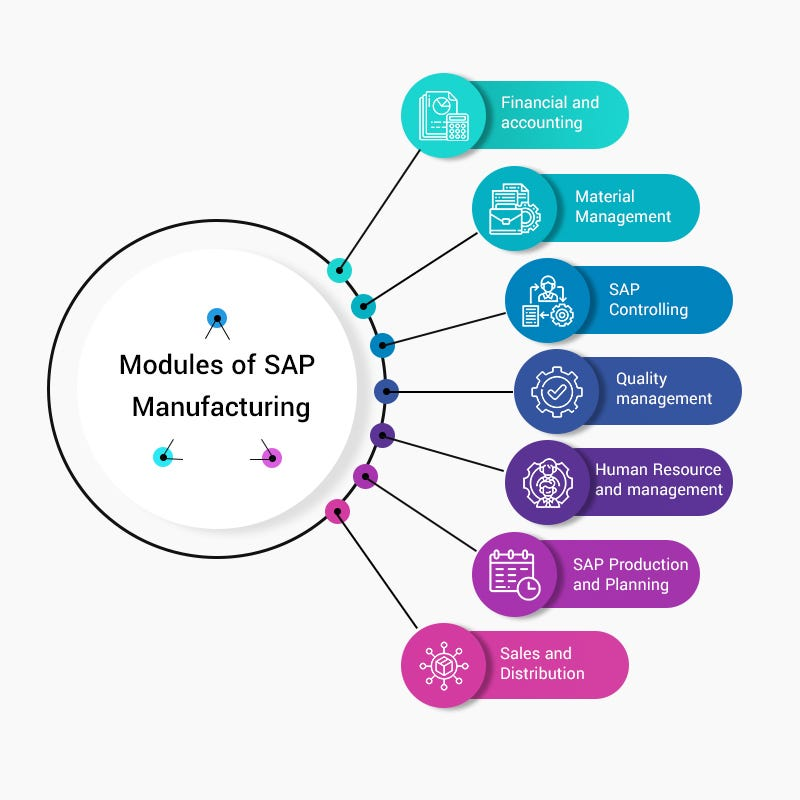
SAP offers a wide range of solutions tailored to the specific needs of the manufacturing industry. These solutions cover various aspects of the manufacturing value chain, from planning and procurement to production, logistics, and customer relationship management (CRM).
1. Production Planning and Execution:
- Demand forecasting and planning: Accurately predict customer demand to optimize production schedules and inventory levels.
- Material requirements planning (MRP): Ensure the availability of necessary materials and components to meet production requirements.
- Production scheduling: Create and manage efficient production plans, considering factors such as capacity, resources, and constraints.
- Shop floor control: Monitor and control production processes in real-time, tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring quality.
- Supplier management: Build strong relationships with suppliers, optimize procurement processes, and ensure timely delivery of materials.
- Inventory management: Maintain optimal inventory levels to balance costs, customer service, and supply chain disruptions.
- Logistics and transportation: Efficiently manage the movement of goods, from raw materials to finished products.
- Supply chain visibility: Gain real-time insights into supply chain operations to improve responsiveness and reduce risks.
3. Quality Management:
- Quality planning: Define quality standards and requirements for products and processes.
- Quality control: Implement inspection and testing procedures to ensure product quality.
- Quality assurance: Monitor and improve product quality throughout the entire lifecycle.
- Quality management systems: Integrate quality management processes with other business functions.
4. Maintenance and Asset Management:
- Predictive maintenance: Use data analytics to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Asset management: Track and manage the lifecycle of assets, from acquisition to disposal.
- Work order management: Plan and execute maintenance activities efficiently.
5. Sales and Customer Relationship Management:
- Sales and order management: Process customer orders accurately and efficiently.
- Customer relationship management: Build strong customer relationships and improve customer satisfaction.
- Sales forecasting: Predict sales trends to optimize production and inventory levels.
Benefits of Implementing SAP in Manufacturing
- Increased efficiency: Streamline processes, reduce manual tasks, and improve productivity.
- Enhanced decision-making: Gain real-time insights into business operations to make informed decisions.
- Improved supply chain visibility: Optimize supply chain performance and reduce costs.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Deliver products and services on time and meet customer expectations.
- Reduced costs: Optimize resource utilization, minimize waste, and improve profitability.
- Compliance with regulations: Ensure adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Overcoming Challenges in SAP Implementation
Implementing SAP can be a complex and challenging process. To ensure successful implementation, manufacturers should consider the following:
- Change management: Address employee resistance to change and provide adequate training.
- Data migration: Migrate data accurately and efficiently from legacy systems to SAP.
- Customization: Balance the need for customization with the benefits of standard SAP functionality.
- Integration: Integrate SAP with other systems and applications to ensure seamless operations.
- Project management: Establish clear project goals, timelines, and responsibilities.
The Future of SAP in Manufacturing Transformation
The manufacturing industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer demands. SAP continues to innovate and develop new solutions to help manufacturers stay ahead of the curve. Some emerging trends in manufacturing include:
- Industry 4.0: Integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Automation of tasks and predictive analytics.
- Blockchain: Secure and transparent supply chain management.
- Additive manufacturing: Production of physical objects from digital designs.
By embracing these trends and leveraging SAP’s capabilities, manufacturers can create intelligent, connected, and sustainable operations.
Conclusion
SAP has become an indispensable tool for manufacturers seeking to transform their businesses. By implementing SAP solutions, manufacturers can improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage. While implementing SAP can be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. By carefully planning and executing the implementation process, manufacturers can reap the rewards of SAP and achieve their business goals.