Introduction
For organizations to remain competitive and make well-informed decisions in the era of digital transformation, smooth data integration across many platforms is essential. Real-time data replication and harmonization are crucial for enterprises utilizing SAP in conjunction with non-SAP systems in order to guarantee consistency, lower latency, and facilitate cross-functional cooperation.
What Is Real-Time Data Replication and Harmonization?
Data Replication
- The technique of moving data from one system to another while maintaining consistency between the source and target systems is known as data replication.
Data Harmonization
- Unifying data from many systems to produce a uniform, consistent perspective is known as data harmonization.
Why Real-Time Matters
- Decision-Making: Facilitates immediate access to current data for improved decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Lowers mistakes and redundancies by ensuring that all systems are operating with the most recent data.
- Customer Experience: Facilitates instantaneous customer communications, including confirmations of transactions and inventory updates.
Importance of Real-Time Data Integration Across SAP and Non-SAP Systems
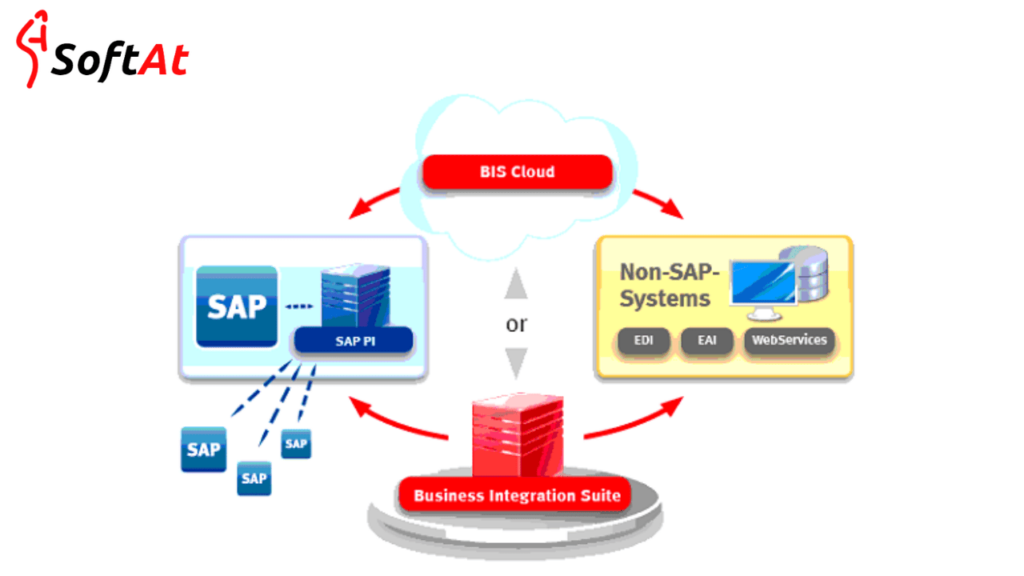
1. Breaking Down Silos
- reduces silos by enabling smooth data flow between SAP and non-SAP systems (such as Oracle, Salesforce, and custom-built platforms).
2. Enabling End-to-End Processes
- enables multi-system procedures such as procure-to-pay and order-to-cash.
3. Enhancing Analytics and Reporting
- Business intelligence solutions are powered by real-time data flows, which provide precise and fast insights.
4. Supporting Multi-cloud Strategies
- Applications are frequently used by modern enterprises in both on-premises and cloud platforms. Data consistency across various landscapes is guaranteed by real-time replication.
Key Tools and Technologies for Real-Time Data Replication and Harmonization
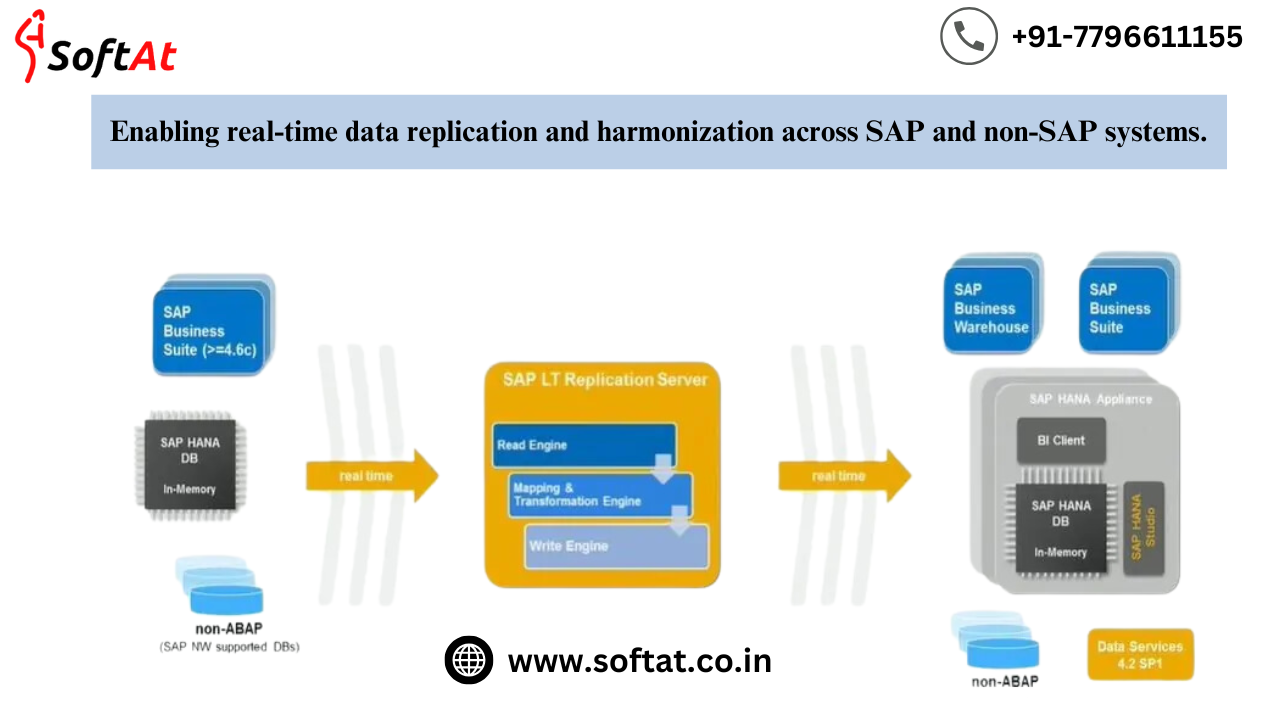
1. SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT)
- Use Case: Instantaneously replicates data from both SAP and non-SAP systems.
- Features: Supports multiple database types, including SQL Server and HANA.
- During replication, data is transformed and filtered.
2. SAP Data Intelligence
- Use Case: Orchestrating data for harmonization and integration.
Features:
- Integrates governance, processing, and data integration.
- connects to a variety of sources, such as third-party systems and SAP.
3. ETL Tools
- Examples: Apache NiFi, Informatica, and Talend.
- Use Case: To harmonize data, extract, transform, and load it.
4. Middleware Solutions
- Examples: MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, and SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI).
- Use Case: serves as a conduit for real-time data transfer between several systems.
5. Change Data Capture (CDC) Tools
- Examples: Qlik Replicate and Oracle GoldenGate
- Use Case: records modifications made to source systems and instantly transfers them to target systems.
How Real-Time Data Replication Works
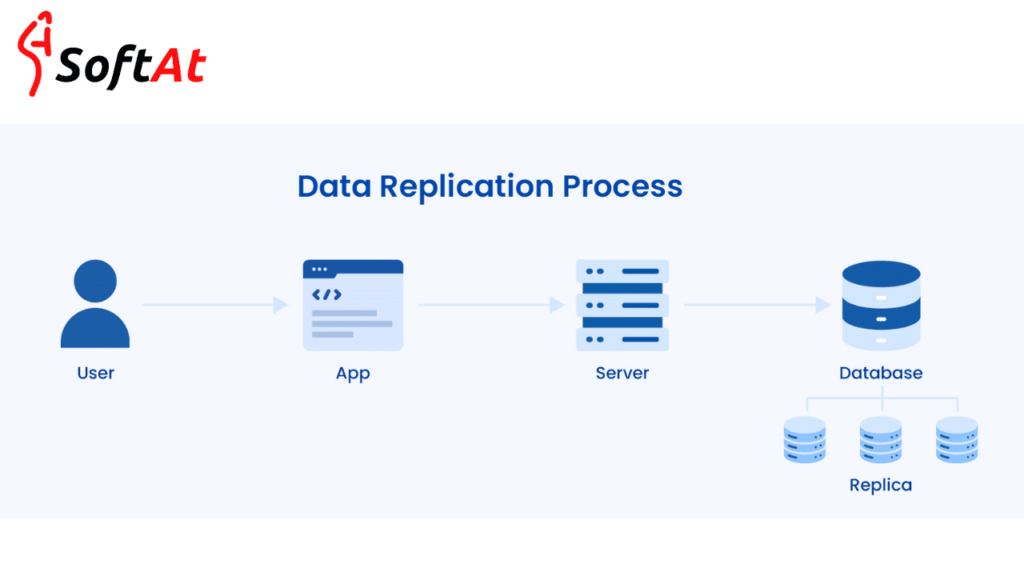
1. Data Extraction
- Use CDC, database triggers, or APIs to retrieve data from the source system.
2. Data Transformation
- Make the required adjustments to conform to the schema of the destination
3. Data Load
- Data Load Input the converted data into the data warehouse or target system
4. Continuous Synchronization
- Polling or event-driven systems can be used to maintain real-time updates.
Steps to Harmonize Data Across Systems
1. Establish Common Data Standards
- Establish schemas, formats, and naming standards to guarantee uniformity.
2. Implement Data Mapping
- To align data structures, map fields between SAP and non-SAP systems.
3. Apply Data Quality Rules
- Prior to replication, use tools for data validation, cleaning, and enrichment.
4. Monitor and Govern Data
- To guarantee data integrity and regulatory compliance, set up monitoring tools.
Challenges in Achieving Real-Time Data Replication and Harmonization
1. System Compatibility
- Different systems may employ protocols or data formats that are incompatible.
- Solution: To fill in the gaps, use adapters or middleware.
2. Network Latency
- To reduce latency, real-time replication needs a strong infrastructure.
- Solution: Make use of data compression and network performance optimization.
3. Data Volume and Complexity
- Managing big datasets might put a burden on available resources.
- Solution: Use CDC and gradual data replication.
4. Security and Compliance Risks
- There are hazards involved with moving sensitive data between systems.
- Solution: Encrypt data while adhering to regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
5. Cost of Implementation
- Projects involving real-time integration may require a lot of resources.
- Solution: Scale gradually, starting with high-priority use cases.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
1. Define Clear Objectives
- Determine the integration project’s primary metrics and business objectives.
2. Choose Scalable Solutions
- Choose technology and tools that will expand to meet your company’s needs.
3. Focus on Data Governance
- Create strong governance guidelines to preserve data compliance and quality.
4. Involve Stakeholders Early
- From the beginning, involve business users, IT departments, and outside partners.
5. Test and Monitor Continuously
- Use monitoring tools to track performance and carry out comprehensive testing during implementation.
Real-World Use Cases of Real-Time Data Integration
1. Supply Chain Visibility
- Scenario: SAP is integrated with third-party logistics systems and Internet of Things sensors by a multinational manufacturer.
- Outcome: Shipment tracking and real-time inventory updates increase productivity and client satisfaction.
2. Financial Consolidation
- Scenario: Financial information from SAP and non-SAP ERP systems is combined by a global corporation.
- Outcome: Accurate, cohesive financial accounts with a quicker month-end closing.
3. E-commerce Integration
- Scenario: A non-SAP e-commerce platform and an online retailer’s SAP inventory are synchronized.
- Outcome: Real-time inventory updates prevent overselling and improve customer trust.
4. Cross-Platform Analytics
- Scenario: A healthcare organization combines data from SAP with analytics software that isn’t SAP.
- Outcome: Up-to-date information on operational metrics and patient care.
Future Trends in Real-Time Data Integration
1. Increased Use of AI and ML
- The automation of data harmonization and anomaly detection will be increasingly aided by AI and ML.
2. Adoption of Data Fabric Architectures
- Access and integration across hybrid landscapes will be made easier with a single data fabric.
3. Real-Time Edge Processing
- IoT-heavy sectors like manufacturing and logistics will be able to replicate data in real time thanks to edge computing.
4. Advanced Security Protocols
- For data integration, concentrate on zero-trust security approaches.
Conclusion
- Businesses that want to remain flexible and competitive must enable real-time data replication and harmonization between SAP and non-SAP systems. Organizations may enhance decision-making, open up new opportunities, and provide value to customers by implementing the appropriate tools, resolving obstacles, and adhering to best practices.
- Investing in real-time data integration is essential to reaching your company objectives, whether they be to improve analytics, optimize supply chains, or increase operational efficiency.
You may be interested in:
A Deep Dive into SAP API Management
Integration cloud system to HANA Cloud Platform using Cloud Connector