SAP SD Module
What is SAP SD?
SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) is an important module of SAP ERP consisting of the business processes required in selling, shipping, and billing a product.
It is a core functional module in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that allows businesses to store and manage customer and product information. This information is used to manage all aspects of a company’s sales, including ordering, shipping, billing, and invoicing.
This module is a part of SAP ECC’s Logistics function and integrates with other modules, including Production Planning (PP), Plant Maintenance (PM), Quality Maintenance (QM), Materials Management (MM), Finance and Controlling (FICO), and Human Resources (HR).
It offers an order-to-cash-cycle business process when used in conjunction with the other modules. According to SAP, SD is in charge of all details throughout the sales and distribution phase of the cycle. It prepares a sales quote, the customer places a sales order, the goods are picked from a warehouse or production facility and transported to the client, an invoice is sent with the order, and accounts receivable settle the payment with the customer in a typical style. Each step generates transactions in this module, which then generates more transactions in the ECC modules.
SAP SD configuration requires adequate knowledge of handling SAP-developed software products. It is widely advised by experts to undertake its training in order to build a strong base of SAP SD Module users. This module has multiple components that integrate different processes within the job area.
Is SAP SD a good career option?
Yes, SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) can be a good career option for individuals interested in pursuing a career in the field of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and sales management. SAP SD is a module within the SAP ERP system that focuses on managing the sales and distribution processes of a company.
Here are a few reasons why SAP SD can be a good career option:
- High Demand: SAP is one of the leading ERP software providers globally, and many companies across various industries use SAP for managing their sales and distribution processes. This creates a high demand for professionals with expertise in SAP SD.
- Wide Range of Job Opportunities: With SAP SD skills, you can explore various job opportunities, including SAP SD consultant, business analyst, functional analyst, solution architect, project manager, or even work as an independent SAP SD consultant.
- Lucrative Salaries: SAP professionals, including those with expertise in SAP SD, often command competitive salaries due to the demand and specialized knowledge required for SAP implementations and support.
- Career Growth and Advancement: As you gain experience and expertise in SAP SD, there are opportunities for career growth and advancement. You can take up leadership roles, work on complex projects, or specialize in specific areas within SAP SD, such as pricing, order management, or logistics execution.
- Continuous Learning: SAP regularly releases updates and new versions of its software, which means that there is a continuous learning curve in SAP SD. This can keep your skills relevant and provide opportunities for professional development.
However, it’s important to note that pursuing a career in SAP SD requires dedication, continuous learning, and staying updated with the latest industry trends. Additionally, obtaining relevant certifications in SAP SD can enhance your career prospects and credibility in the job market.
Key Components
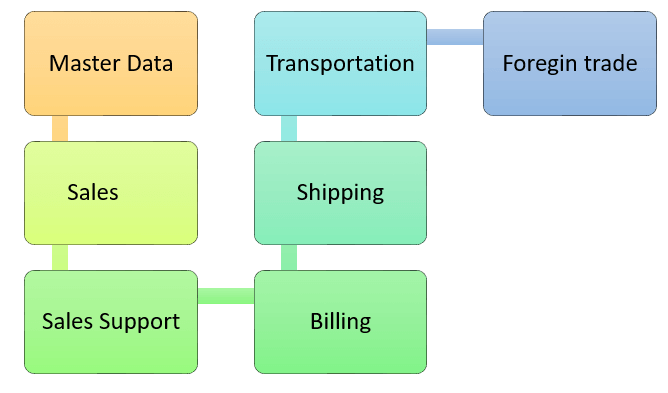
This module is the most important ERP module developed by SAP. It helps in better management of sales and customer distribution data and processes in organizations. The important components are:
- Master Data
- Sales
- Shipping of Material
- Billing-Related
- Sales support
- Transportation of products
- Foreign Trade
SAP-SD-MD (Master Data)
Master data is included in SAP SD user, and the procedure entails tracking each and every transaction inside the data. Customer master data, material master data, price conditions records, production records, and credit management are all parts of the sales and distribution master data. This module records the whole flow of information from order to cash.
Functions of master data
Master data is the most important factor in the Sales and Distribution module
There are two levels of master’s in SD:
- Customer Master
- Material Master
- Pricing Conditions
While the second-level master store looks like this:
- Detailed information about customers, materials, and business partners.
- Flexible data structures support the business environment.
SAP-SD-SLS (Sales)
As the term suggests, SAP SD sales handle minute details of every sale that is taken place. From recording the product to customer details, pricing, feedback, and the sales process, everything is tracked through this module.
Functions of Sales Module
- Inquiries & Quotes
- Sales Orders
- Consignment
- Scheduling Agreements
- Rush Orders and Back Orders
- Credit & Debit Memo Requests
SHP (Shipping)
Sales are closely related to shipping and delivery. A Product needs to be rightly shipped and delivered to the customer. There are different methods of shipping and this module track each one used for each delivery. The entire process from being shipped to delivered or returned back is recorded through this module.
BIL (Billing Module)
Billing is a major part of sales. Customers can pay either online using a debit or credit card, through cash on delivery, or by using a PayPal account, and so on. To maintain a proper track for future reference, each bill detailed is recorded through this module.
Sales Support
From selling a product to maintaining it for a process, customers constantly interact with the sales team. The data exchanged between the sales team and customers while delivering support for a product is recorded and reported through this module. It offers functionality to support staff, which are involved in business development and customer service-related processes.
Functions of Sales Support:
- Sales Prospects
- Contact Persons
- Competitors and Competitive Products
- Sales and Activities
- Direct Marketing
TBA (Transportation)
This SAP SD component works closely with the above shipping module. A product can be either couriered or manually delivered. The mode of transportation is different for each one and is being tracked through this module.
Features of Transportation:
- It is a flexible and easy-to-use component that enables you to collect, consolidate, and utilize data from sales and distribution processing.
- It is widely used for (LIS) Logistic Information System.
FTT (Foreign Trade)
This component helps a department to handle the data related to foreign trade including both imported products and products exported outside. It works best for enterprises involved with trade across nations.
Advantages
- Track sales transactions
- Track sales data along with team performance
- Record pre-sale and post-sale process
- Defined process for sales and distribution
- Helps you to categorize diverse sales and process
- Effective management of sales documents in a specific system
Features of SAP SD Module
- Price & Taxation: It helps you to evaluate the price of goods and services under various conditions like rebate or discount, which is granted to a customer.
- Availability Check: Check the availability of a product in the warehouse of an organization.
- Billing & Invoice: Helps you to generate bills or invoices.
- Material Determination: This helps you to determine the details of materials on the basis of a certain condition.
- Credit Management: It is a method of managing the credit limits of customers. It can be figured in two different ways i.e., simple credit check and automatic credit check.
- Account Determination: This helps you to determine the details of customers on the basis of a given condition type.
SAP SD Module Pricing procedure
The pricing method in SAP SD aids in determining the right prices in sales documents. This technique allows you to assign various sorts of computations to various needs. The pricing procedure determines all conditions in a single procedure and gets a net amount using the sub-total.
What are the SD SAP processes?
SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) encompasses various processes that facilitate the sales and distribution functions within an organization. Here are the key processes within SAP SD:
- Sales Order Processing: This process involves creating and managing sales orders. It includes functions such as order entry, order confirmation, availability check, pricing, credit check, and delivery schedule.
- Pricing and Conditions: SAP SD allows for complex pricing calculations based on various factors such as customer pricing agreements, discounts, surcharges, taxes, and promotions. Pricing conditions can be defined and maintained within the system.
- Availability Check: The availability check ensures that the ordered products or materials are available in the required quantity at the requested delivery date. It considers factors such as stock availability, backorders, and production lead times.
- Delivery Processing: This process involves managing the physical delivery of products to customers. It includes functions such as picking, packing, and goods issues. Delivery documents, such as delivery notes and packing lists, are generated in this process.
- Transportation and Shipment: SAP SD provides functionality for managing transportation and shipment processes. It includes features for route determination, carrier selection, transportation planning, and tracking.
- Billing and Invoicing: In this process, customer billing and invoicing are handled. It includes generating billing documents, such as invoices, credit notes, and debit notes, based on sales orders and deliveries.
- Sales Support: SAP SD also supports sales support activities, such as quotation management, contract management, and sales information systems. These functions help in tracking sales activities, managing customer inquiries, and providing pre-sales support.
- Returns and Complaints: SAP SD facilitates the handling of returns, product exchanges, and customer complaints. It includes processes for return order processing, return delivery, credit memo processing, and complaint handling.
- Credit Management: Credit management in SAP SD involves evaluating and monitoring the creditworthiness of customers, managing credit limits, and handling credit holds and credit blocks to ensure timely and secure payments.
- Sales Analytics and Reporting: SAP SD provides reporting and analytics capabilities to monitor sales performance, track key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze sales trends, and generate sales-related reports for decision-making purposes.
These are the main processes within SAP SD, but it’s important to note that the module is highly configurable and can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of an organization’s sales and distribution operations.
SAD SD Account Determination
Each pricing element’s revenue, discount, and tax values are posted to their appropriate G/L accounts via SAP. The system employs conditional logic to find the correct G/L account, a process known as account determination.
How does SAP determine account determination?
The system automatically determines account determination based on the following configuration:
- Chart of Accounts
- Sales Organisation
- Customer Account grp (Payer Customer Master records)
- Material Account grp (Material Master)
- Account key





