What are SAP Projects?
SAP Projects are on a lot of riding. As a result, a single blunder will cost you a lot of money. A poor SAP deployment will result in a negative customer experience, brand harm, significant revenue loss, and exorbitant operational costs. As a result, having the best SAP Projects is critical.
In this post, you’ll learn everything there is to know about SAP implementation projects and other SAP projects, including how they work, their benefits, and their drawbacks.
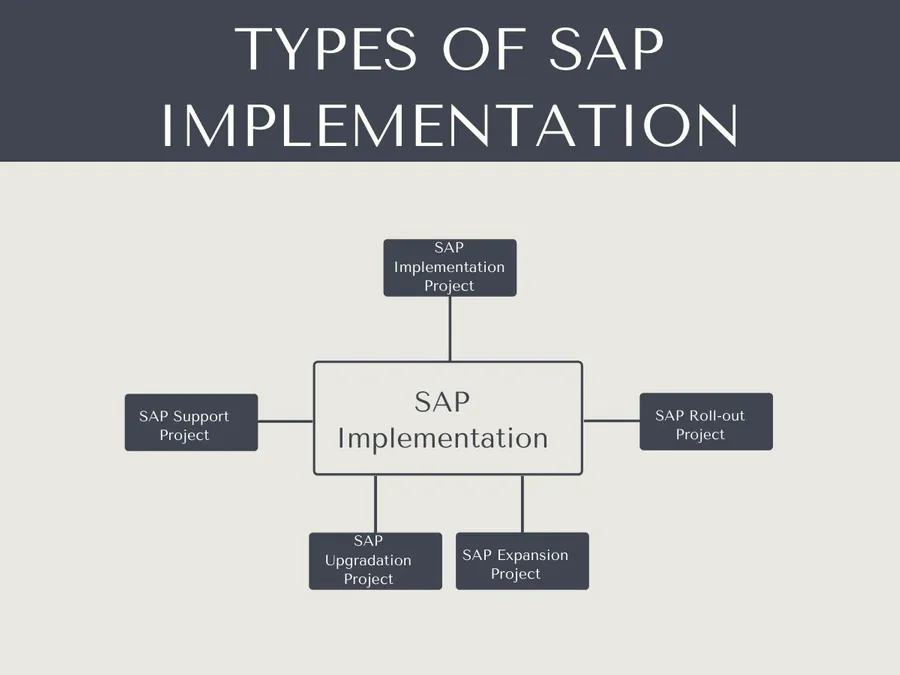
Types of SAP Projects
1)SAP Implementation Project: It is a set of best practices and workflows for designing, tuning, and constructing an SAP landscape.
2)SAP Support Project: In this, the team handles the issues and queries of users, using an already implemented SAP system.
3)SAP Roll-out Project: It means repurposing the existing implementation business process and cycle at a new site.
4)SAP Upgradation Project: It is being done with the goal of upgrading the present system to the most recent SAP release.
5)SAP Expansion Project: It refers to expanding the existing systems to new locations, companies, and departments.
1)SAP Implementation Project
The collective methods and workflows used to establish, construct, and tune an SAP landscape are referred to as SAP implementation. Every SAP implementation is different. The initiative aims to achieve high-level objectives such as improved collaboration and a higher return on information. As a result, SAP implementation projects necessitate meticulous preparation and execution using a proven methodology.
Let’s take a look at the many phases or steps that make up an SAP implementation project.
1)Project Preparation: In this, you’ll start by determining the scope, priorities, and objectives for SAP. Your goal is to gain stakeholder support while allocating resources.
2)Business Blueprint: This step is all about defining the business process for landscape address.
3)Realization: It is at this point that the project’s implementation begins. You’ll begin developing, testing, and improving the landscape using the business blueprint. The work of the functional team will come to an end at this point, and the technical team will take over.
4)Final Preparation: Now, it’s the right time to be fully prepared for migration and go live.
5)Go-Live Support: In short, this means flipping the switch to look after the newly implemented landscape project of SAP.
There are two common methods of SAP implementation. They are:
1)Big Bang Implementation
2)Phased Project
Big Bang Implementation
All of your computer systems will begin using the project on the same day if Big Bang is implemented. In a nutshell, all of the medals will be available at the same moment. It’s the same as turning off your old computer and immediately switching to the new one.
Organizations typically choose this implementation method since it is a faster and less expensive choice. Detailed and end-to-end testing, as well as data validation, can help you find problems and errors, but they will never help you understand the problem in a single area.
Phased Project
You’ll use this method to roll out the program in a sequential manner, introducing the new software piece by piece. The phased project does not have a single large go-live date, but rather a series of smaller ones. As a result, your system and staff will have more time to adjust to the changes.
2)SAP Support Project
Since it manages tickets, the SAP support project is also known as an issue tracking system. Under this project, end-user mistakes and defects are submitted to the support staff, who categorizes them into low, medium, and high severity levels.
For example, a corporation may upgrade its software on a regular basis, shifting from outdated to newer versions (4.5, 4.6 ECC5 to ECC6). In these circumstances, the support staff will work with the entire company to improve SAP installation.
We need to rectify the error between the durations because each level of severity has its own duration to fix.
This project’s benefits and drawbacks are similar to those of SAP implementation projects. No one can deny, however, that the SAP support project is the bedrock for expanding functionality and increasing SAP expertise among the user community. Demonstrate consideration for your position. By adopting an SAP support project, you can strive to optimize SAP and surrounding business processes in order to improve user happiness.
3)SAP Roll-Out Project
The SAP rollout project entails repurposing the old deployment cycle and business operations in a new location.
For example, suppose a corporation develops a global template solution and only implements it in a few regions. An SAP roll-out project is defined as a project that adds local procedures to the solution of another location and then goes live again.
For this project, you’ll need to make some basic adjustments based on the implementation location. There is no need to start from the beginning. You only need to focus on logos, company codes, and printouts. Change the personnel integration and management as needed to meet the company’s needs.
4)SAP Upgradation Project
It is a process that firms undertake on a regular basis to upgrade their system to the most recent version. The company’s purpose for this project is to upgrade and cover the evolution of the SAP technical enhancement package on a technical level.
If a corporation wants to upgrade to SAP ERP 6.0, for example, this project must be implemented. As the business grows, it will need to upgrade its operating system, hardware, and database platform. They also need to convert the data to Unicode.
This upgrade project gives businesses the option of choosing between two strategies: resource minimization and downtime minimization. After a thorough examination of technical issues and economic requirements, the technical team must choose this method for this project.
Steps involved under the SAP Upgradation project are:
1. System Preparation
2. SPDD Phase
2. Upgradation of the system
4. SPAU Phase
5. Testing
6. Z programs
7. Post-program upgrade activities
5)SAP Expansion Project
During the company’s boom years, every company chooses the SAP expansion project. However, there are several circumstances in which a business must choose this SAP project, such as:
1. During the acquisition of a new company in the same industry.
2. When a new branch is opened at a new geographical location.
3. When a business requires a new logistics and allocation plant as a result of the addition of new facilities.
These scenarios involve the company expanding or growing. As a result, the SAP expansion project must be implemented.
SAP Project System in SAP Projects
SAP Project System (PS) is a component of SAP’s Project and Portfolio Management solution. Project System assists in project management throughout the full project lifecycle, from project conception to detailed planning, execution, and completion.
The SAP PS Module can be used for big and complicated projects such as building, production, service, and investment projects in all industries because of its strong connection with SAP’s Finance and Logistics modules.
One of SAP PS’s advantages as a project management tool is that it can be combined with other SAP modules, as well as with non-SAP project management tools like Primavera and Microsoft Project.
Companies start using SAP Project System (PS) in order to gain advantage from subjects below:
1. Project profitability by phase.
2. Resource utilization rates.
3. Organized and detailed follow-up of consumer and company in-house projects.
4. One common platform for project office, logistics units, and finance department.
SAP Project System Module
Integration
SAP PS is fully integrated with SAP HCM (Human Capital Management), SAP SD (Sales & Distribution), SAP PP (Production Planning), SAP PM (Plant Maintenance), SAP FICO (Financial Accounting), SAP IM (Investment Management), SAP MM (Material Management), and other SAP R/3 modules. PS’s connection with other modules makes it possible to plan and execute all of a project’s duties. PS module can access data from all departments participating in a project and delivers consistent real-time data as a result of integration, for instance.
Functions
1. Project Structure: It is the process of creating work packages for projects utilizing SAP PS’s Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Elements and Network Plans.
2. Time Schedule: It is the process of using SAP PS’s Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Elements and Network Plans to create work packages for projects.
3. Budgeting: It is the budgeting of projects and the steps in work packages (WBS elements) that are included in the projects, as it manages budgets and maintains budget availability restrictions.
4. Cost and Revenue Planning: It is the cost and revenue planning of the steps in work packages (WBS elements).
5. Project Progress Analysis: It involves the analysis of the stages of the projects, the progress of the project steps, and the project status.
6. Reporting: It is the provision of various reporting based on hierarchical, financial (G/L Account and line item), material, resource, and project progress regarding the projects.