Introduction
Many are using public cloud platforms to host their SAP systems as more companies embrace cloud technologies to spur innovation. The top options for managing SAP workloads are Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS), each of which has unique benefits in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and performance.
1. Why Move SAP to the Cloud?
a. Scalability
On-demand scalability provided by cloud platforms enables companies to modify resources in accordance with workload demands.
b. Cost Efficiency
Because cloud hosting offers pay-as-you-go pricing options, it does away with the requirement for expensive on-premises infrastructure.
c. Performance Optimization
Advanced computer power and fast networks improve SAP application performance..
d. Business Continuity
Cloud systems for business continuity offer strong backup and disaster recovery options to guarantee less downtime.
2. SAP on AWS
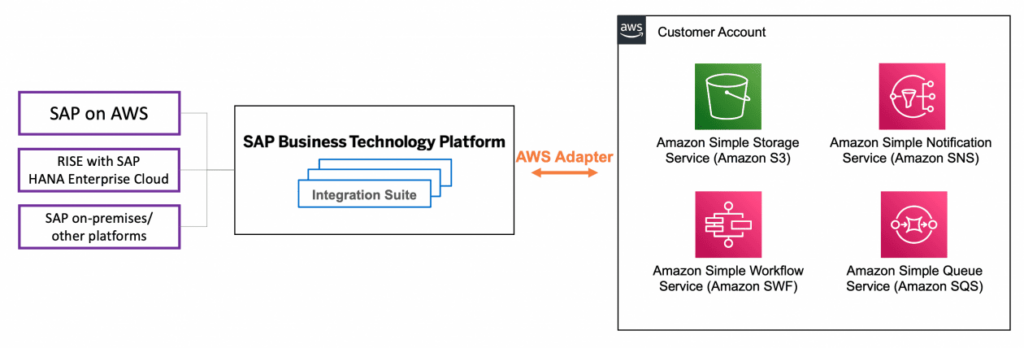
a. Key Features
- SAP-Certified Instances: SAP-Certified Instances: EC2 instances tailored for SAP workloads, such as HANA databases, are available from AWS.
- Automation Tools: Tasks related to deployment and management are automated by services such as AWS Systems Manager..
- Global Infrastructure: 32 regions and 102 availability zones provide a wide global reach.
b. Benefits
- Flexibility: A wide variety of instance sizes and types to accommodate different SAP applications.
- Combining: Simple interaction with other AWS services, such as Lambda for automation or S3 for storage.
- Security: Adherence to international standards and thorough security controls.
c. Use Case
By moving its SAP S/4HANA system to AWS and utilizing high-performance computing and analytics, a multinational retailer increased the effectiveness of its supply chain.
3. SAP on Microsoft Azure
a. Key Features
- SAP on Azure Large Instances: Dedicated virtual machines for workloads including SAP HANA.
- Seamless Integration with Microsoft Tools: Office 365, Teams, and Dynamics 365 are natively supported.
- Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: SAP workloads can be deployed hybridly thanks to Azure Arc.
b. Benefits
- Enterprise Focus: Personalized solutions for businesses with intricate SAP setups.
- Reliability: High availability and resolute SLA obligations.
- Analytics and AI Integration: For deeper insights, use Azure Synapse Analytics and AI..
c. Use Case
By combining SAP ERP on Azure with Power BI for real-time analytics, a manufacturing company was able to optimize its operations.
4. SAP on Google Cloud
a. Key Features
- Compute-Optimized VMs: Instances designed for workloads requiring a lot of memory, such as SAP HANA.
- Advanced AI/ML Capabilities: Innovative application cases through integration with BigQuery and TensorFlow.
- Network Infrastructure: The performance of applications is improved by Google’s low-latency network.
b. Benefits
- Data Analytics Excellence: Big data and analytics native tools.
- Sustainability: Google’s dedication to cloud operations that are carbon neutral.
- Pricing Transparency: Competitive and straightforward pricing schemes.
c. Use Case
In order to move its SAP systems, a financial services company used Google Cloud, which offered safe infrastructure and sophisticated analytics.
5. Comparison: AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud for SAP
| Feature | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Presence | Largest number of regions/zones | Extensive coverage, particularly in hybrid models | Growing rapidly with strong global reach |
| Instance Variety | Broadest range of SAP-certified instances | Optimized large instances for SAP | Focus on compute-optimized VMs |
| Integration | Deep integration with AWS ecosystem | Seamless with Microsoft tools | Advanced AI/ML and analytics tools |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly management tools | Strong enterprise focus | Developer-friendly with innovation tools |
| Cost Efficiency | Pay-as-you-go, volume discounts | Flexible pricing models | Transparent and competitive pricing |
6. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cloud Provider for SAP
a. Performance Requirements
Analyze your SAP apps’ memory, processing, and storage requirements.
b. Compliance Standards
Verify that the platform complies with industry-specific laws such as ISO 27001, GDPR, or HIPAA.
c. Integration Needs
Think about how the platform works with the tools and systems you already have.
d. Cost Analysis
Examine the price structures, taking into account unforeseen expenses such as storage or data transmission charges.
e. Support Services
Evaluate the provider’s technical support and training offerings.
7. Steps to Migrate SAP to the Cloud
Step 1: Assessment and Planning
- Evaluate the preparedness of your current SAP systems.
- Determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) and migration objectives.
Step 2: Select a Cloud Provider
- Depending on your needs, pick between Google Cloud, AWS, or Azure.
Step 3: Proof of Concept (PoC)
- Perform a pilot migration to validate the process and resolve any challenges.
Step 4: Data Migration
- Use cloud-native tools like AWS Snowball, Azure Migrate, or Google Transfer Appliance.
Step 5: Testing and Validation
- To guarantee seamless operations, test all features, integrations, and workflows.
Step 6: Go-Live and Optimization
- Install the SAP system and keep an eye on its functioning.
8. Best Practices for SAP Cloud Migration
a. Invest in Training
Train your IT team on the chosen cloud platform to maximize efficiency.
b. Adopt a Phased Approach
Migrate workloads incrementally to minimize risks and disruptions.
c. Leverage Cloud-Native Tools
Utilize the tools and services offered by the cloud provider for automation and optimization.
d. Monitor Continuously
Implement robust monitoring systems to track performance and security metrics.
9. Future Trends in SAP Cloud Hosting
a. Multi-Cloud Strategies
Businesses are using multi-cloud strategies more frequently in order to reduce risk and increase flexibility.
b. AI and Machine Learning
using AI and ML to automate processes and do predictive analytics.
c. Sustainability Initiatives
To lessen their carbon footprints, cloud companies are concentrating on green computing.
d. Edge Computing
utilizing edge computing to improve SAP applications’ performance in distant areas..
Conclusion
Migrating SAP to the cloud is a transformative step that can enhance efficiency, scalability, and innovation. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud each bring unique strengths to the table, catering to diverse business needs. By assessing your organization’s requirements and aligning them with the capabilities of these platforms, you can ensure a successful migration and unlock the full potential of SAP in the cloud.
You may be interested in:
A Deep Dive into SAP API Management
Integration cloud system to HANA Cloud Platform using Cloud Connector