What is SAP FICO?
SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) is a critical core functional component of SAP ERP Central Component that helps businesses to handle all of their financial data. SAP FICO enables businesses to keep a detailed record of their financial transactions. SAP FICO is designed to assist firms in generating and managing financial statements for analysis and reporting, as well as in successful business planning and decision-making. SAP Finance
SAP FICO is divided into two parts: SAP Finance (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO). Each one is used in a certain financial transaction. SAP FI is responsible for comprehensive financial reporting and accounting, whereas SAP CO is responsible for cost planning and monitoring. SAP FI and SAP CO were launched as different modules at first, but they are now so closely integrated that many people refer to them as one.
SAP Finance
SAP FI modules
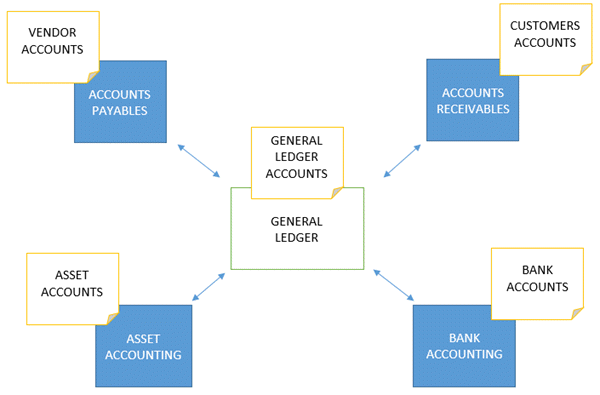
SAP FI is made up of SAP FICO sub-modules. All the sub-modules are interconnected and work together in real-time. Because all of the sub-modules are connected, a trial balance can be extracted at any time and it will always balance.
General Ledger Accounting
General ledger accounting is used to manage all general ledger accounts that are used for reporting. A chart of accounts is a collection of all general ledger accounts used by a firm or a group of enterprises in SAP. These are the accounts that will be used in the financial statement preparation. The majority of transactions are recorded in sub-modules and reconciled in real-time with the general ledgers. Journal vouchers, which are posted to alter or correct transactions, are an example of transactions that can be done directly in general ledger accounting. General ledger accounting can also be used to perform reversals. Trial balances can be taken from the system and balances in general ledger accounts can be presented. SAP Finance
Accounts receivables
Accounts receivables is a sub-module in FICO SAP that records all client transactions and manages customer accounts. Customer accounts will be kept separate, and when transactions are posted to consumer accounts, reconciliation accounts in the general ledger will be updated in real-time with the figures. Invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payment, dunning, and executing customer reports are all transactions in account receivables.
Accounts payables
Accounts payables is a sub-module that records all vendor transactions and keeps track of vendor accounts. Vendor accounts are kept separate, and when transactions are posted in customer accounts, reconciliation accounts in the general ledger are updated in real-time with the figures. Invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payment, automatic payment program, and executing vendor reports are all transactions in account payables.
Asset accounting
Asset accounting in FICO SAP keeps track of all transactions involving an entity’s assets. Reconciliation accounts in the general ledger are updated in real-time when transactions are posted in asset accounts. Asset purchase, asset retirement, asset sale, asset transfer, asset revaluation, and asset depreciation are all transactions in asset accounting.
Bank accounting
Bank accounting records all transactions with the banks. Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing all transactions on bank statements to transactions in the system and reconciling them.
All SAP FI sub-modules are integrated, and transactions are updated in real-time, allowing for the extraction of accurate financial statements at any moment.
SAP CO modules
SAP CO enables processes to plan, report on, and monitor costs from business activities, whereas SAP FI deals with a company’s accounting and internal & external reporting. SAP CO can help you increase your company’s profitability. SAP CO can help you increase your company’s profitability. SAP CO, like SAP FI, is made up of sub-modules that deal with the various processes:
Cost Elements
It provides an overview of all the company’s costs and revenues based on profit and loss statements – also known as income statements. The genesis of expenses is described by cost element accounting. Specific costs incurred by the company are represented by cost factors.
Cost centers
It is concerned with the costs of the company’s internal divisions or departments, such as sales, production, marketing, and human resources. Cost centers are only concerned with expenses, not revenues.
Profit centers
It manages all of the expense data for the company’s many business lines. Unlike cost centers, which solely deal with expenses, it deals with both expenses and income.
Profitability analysis
It gives the business the capacity to assess the profitability of its products. Profitability Analysis, for example, can help you make decisions about product price, distribution routes, and target market segments. It also enables another level of analysis, such as profitability for each region or country, product kinds & distribution routes, or individual customers.
Product costing
It keeps track of the costs of producing the company’s goods and services. Product costing analysis can assist in the management of production costs and efficiencies.
SAP FICO Consultant
An SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) consultant creates, implements, and maintains SAP-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Understanding an organization’s business requirements, teaching end-users, and resolving out end-users day-to-day queries are all tasks of this professional. The ability to multitask, knowledge of accounting business processes, and past work experience in professional services or distribution organizations are all required qualifications for the position.
Responsibilities of FICO (Finance and Controlling) consultant
Here are some examples of responsibilities taken from genuine fico sap consultant resumes that depict typical tasks people would accomplish in their positions:
- Collect requirements with business management, prepare as-is to-be, configuration modifications, unit testing, and data conversion process.
- Configure COPA profiles based on order types to satisfy your company’s profitability analysis needs.
- Define the lockbox control parameters and the posting data in the global settings for electronic bank statements.
- Business practises should be mapped to ERP software.
- In the CO-PC module, create new activity kinds for the client.
- Examine the current system and compile a list of functional requirements for the future system.
- Examine the functional and technical designs of the ABAP/4 team for clarity and completeness.
- Create a BDC application that uses transaction ABAA to upload unplanned depreciation for numerous assets.
- Participate actively in the configuration of FI-GL, FI-AP, and FI-AR module discrepancies.
- Analyze the problems involve in PCA balancing, and make the required changes in the PCA balancing custom programs.
Is SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) a good career?
Here are some reasons why SAP FICO can be a good career choice:
- High Demand: SAP FICO professionals are in demand across various industries as finance and accounting are critical functions in every organization. Businesses require experts to manage their financial processes, reporting, and compliance using SAP’s powerful ERP system.
- Competitive Salary: Due to the specialized nature of SAP FICO skills, professionals in this field often command competitive salaries compared to other finance or IT roles.
- Job Stability: SAP FICO plays a central role in an organization’s financial management, making these roles relatively stable, especially in companies that rely on SAP ERP systems.
- Opportunities for Growth: A career in SAP FICO can lead to various growth opportunities within an organization, such as becoming a team lead, functional consultant, or project manager.
- Cross-Industry Applicability: SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) skills are transferable across different industries, enabling professionals to explore diverse sectors and career paths.
- Continuous Learning: SAP regularly updates and enhances its software, so SAP FICO professionals have opportunities to learn and work with the latest technologies and functionalities.
- International Opportunities: SAP FICO is used by organizations worldwide, providing potential opportunities for global assignments and working in multicultural environments.
However, it’s essential to consider a few aspects before pursuing a career in SAP FICO:
- Technical and Functional Skills: SAP FICO involves a mix of technical and functional expertise. Aspiring professionals should be comfortable with both financial and accounting concepts and SAP’s software.
- Continuous Learning: SAP FICO professionals need to stay updated with the latest advancements and changes in SAP technologies and financial regulations.
- Work Experience: While entry-level opportunities may be available, many higher-level positions may require relevant work experience or a combination of SAP expertise and industry experience.
- Job Market Trends: As technology evolves, the demand for specific SAP modules might change. It’s essential to research current job market trends and the demand for SAP FICO in your region.
Ultimately, whether SAP FICO is a good career choice for you depends on your interests, background, and long-term career goals. If you have an aptitude for finance, a passion for technology, and enjoy problem-solving, a career in SAP FICO could be a rewarding and fulfilling path. To make an informed decision, consider speaking with SAP professionals, career counselors, or recruiters to gain insights into the job market and potential career growth opportunities in SAP FICO.





