Introduction
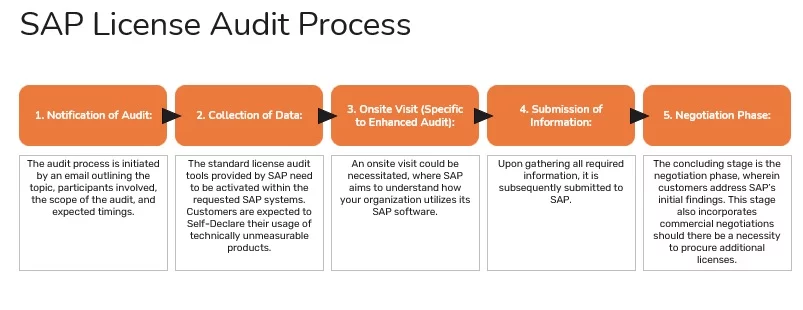
SAP, a complex enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, is the backbone of many organizations. Its intricate structure and vast data repository make it a critical target for audits. An SAP audit is a systematic examination of an organization’s SAP system to assess its compliance with internal controls, financial regulations, and industry standards. It’s a crucial process that ensures data integrity, accuracy, and security.
This blog will delve deep into the intricacies of SAP audits, covering their purpose, types, key areas of focus, and best practices for preparation and execution.
Why SAP Audits Matter
SAP audits serve multiple purposes:
- Risk mitigation: Identifies potential vulnerabilities and threats to the system.
- Compliance assurance: Verifies adherence to regulations like SOX, GDPR, and industry-specific standards.
- Data integrity: Ensures data accuracy and reliability.
- Process efficiency: Optimizes SAP processes for better performance.
- Fraud prevention: Detects anomalies and potential fraudulent activities.
Types of SAP Audits
SAP audits can be categorized based on their scope and objectives:
- Financial audits: Focus on financial transactions, revenue recognition, and expense management.
- IT general controls audits: Assess the overall IT environment, including access controls, system development, and change management.
- Operational audits: Evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of SAP processes.
- Compliance audits: Verify adherence to specific regulations and industry standards.
- Security audits: Assess the system’s security measures to protect sensitive data.
Key Areas of an SAP Audit
A comprehensive SAP audit typically covers the following areas:
- Master data: Verifies the accuracy and completeness of customer, vendor, and material data.
- Transaction data: Examines sales, purchasing, inventory, and financial transactions for accuracy and compliance.
- User access and authorization: Evaluates access controls to prevent unauthorized access and data manipulation.
- Custom development: Reviews custom programs for compliance with coding standards and security best practices.
- Change management: Assesses the change management process for SAP system modifications.
- Reporting and analytics: Evaluates the accuracy and reliability of financial and operational reports.
- Integration with other systems: Checks data flow and consistency between SAP and external systems.
Preparing for an SAP Audit
Effective audit preparation is essential for a smooth process. Key steps include:
- Risk assessment: Identify potential audit areas based on business processes and regulatory requirements.
- Documentation: Gather relevant documentation, such as policies, procedures, and system configurations.
- Data cleansing: Ensure data accuracy and completeness before the audit.
- User training: Educate employees about audit procedures and their responsibilities.
- Audit committee involvement: Establish an audit committee to oversee the process.
Conducting an SAP Audit
The audit process involves several stages:
- Planning: Define audit objectives, scope, and methodology.
- Fieldwork: Collect audit evidence through testing, interviews, and document review.
- Reporting: Prepare a comprehensive audit report outlining findings, recommendations, and action plans.
- Follow-up: Monitor implementation of corrective actions.
Best Practices for SAP Audits
To maximize the effectiveness of SAP audits, consider these best practices:
- Continuous monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring tools to identify potential issues.
- Automation: Utilize automation for repetitive audit tasks.
- Data analytics: Leverage data analytics to uncover trends and anomalies.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT and business departments.
- Post-audit review: Conduct regular reviews of audit findings and recommendations.
Conclusion
SAP audits are critical for maintaining the integrity and security of an organization’s ERP system. By understanding the different types of audits, key areas of focus, and best practices, businesses can effectively prepare for and conduct audits, mitigating risks, ensuring compliance, and optimizing SAP operations.
Note: This blog provides a general overview of SAP audits. Specific requirements and procedures may vary based on industry, company size, and regulatory environment.
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN
Best Practices for SAP Cloud Platform Development: A Comprehensive Guide




