Introduction
Mechanical Cycle Robotization (RPA) is altering the way that organizations handle dull, rule-based undertakings via mechanizing work processes and working on functional effectiveness. In SAP conditions, where errands like information passage, report age, and cycle checking are continuous, RPA offers an amazing chance to smooth out tasks, diminish mistakes, and let loose HR for additional essential exercises.
Understanding RPA in the Context of SAP
What is RPA?
- RPA includes utilizing programming robots or “bots” to perform organized and tedious undertakings across different frameworks and applications, mirroring human activities, for example, signing in, replicating information, or creating reports.
Why RPA for SAP?
- SAP systems manage critical business functions, but tasks often require manual intervention, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. RPA can seamlessly interact with SAP systems to automate these processes without modifying the underlying architecture.
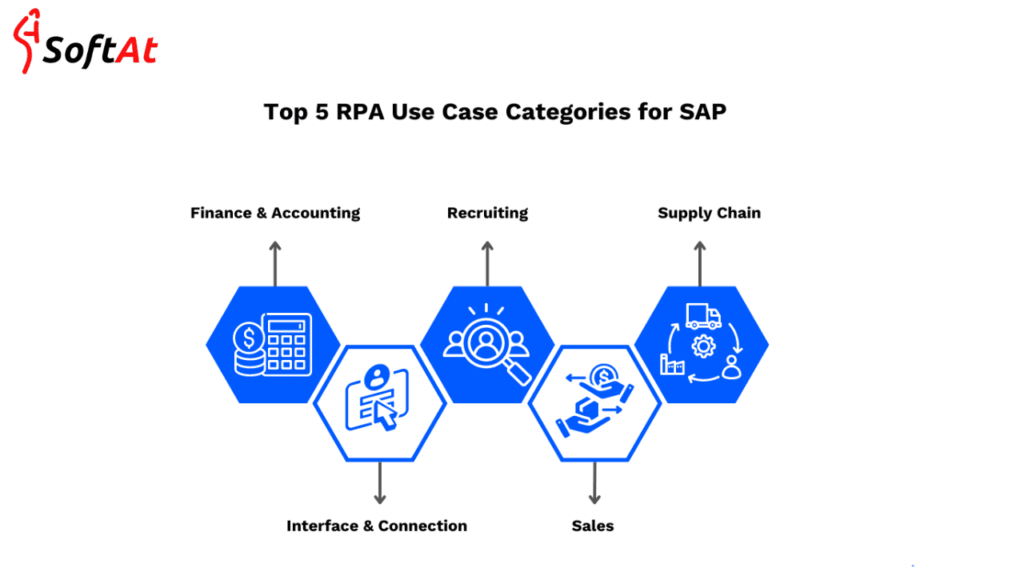
Key SAP Tasks That RPA Can Automate
1. Data Entry
- automating the process of entering vast amounts of data into SAP modules, like logistics and finance.
- For instance, uploading inventory information or vendor details.
2. Report Generation
- obtaining, structuring, and disseminating data from SAP to stakeholders.
- For instance, sales performance summaries or monthly financial reports.
3. Invoice Processing
- automating the process of extracting, validating, and entering invoice data into SAP.
4. Order Management
- handling sales orders, including updating statuses and validating data.
5. HR Operations
- automating the workflows for leave management, employee onboarding, and payroll processing.
6. Master Data Management
- automated modifications to master data records in order to guarantee data consistency.
Benefits of Using RPA in SAP
1. Improved Accuracy
- minimizes errors brought on by repetitive operations and manual data entering.
2. Increased Efficiency
- Speeds up processes that are traditionally time-consuming.
3. Cost Savings
- reduces reliance on physical labor for repetitive operations, which lowers operating expenses.
4. Scalability
- Bots may be readily scaled to accommodate growing workloads without the need to hire more employees.
5. Enhanced Compliance
- keeps accurate and consistent records to guarantee compliance with regulations.
6. Better Employee Productivity
- enables workers to concentrate on valuable and strategic work rather than repetitive duties.
How RPA Integrates with SAP
1. Non-invasive Integration
- RPA tools don’t require modifications to the underlying SAP systems; they operate at the user interface level.
2. Connectivity with APIs
- For quicker and more seamless operation, bots can communicate with SAP systems via APIs.
3. Compatibility with Different SAP Versions
- works with SAP S/4HANA, SAP ECC, and legacy SAP systems.
Popular RPA Tools for SAP Automation
1. UiPath
- provides pre-made SAP automation interfaces.
- includes integration and automation features for SAP GUI.
2. Blue Prism
- dependable platform for SAP workflow automation.
3. Automation Anywhere
- offers a range of solutions, such as data processing and extraction, for smooth SAP automation.
4. SAP Intelligent RPA
- With native interaction with SAP systems, it was created especially for SAP settings.
Implementing RPA for SAP: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Identify Repetitive Tasks
- To find high-volume, rule-based jobs that can be automated, conduct a process assessment.
Step 2: Choose the Right RPA Tool
- Consider scalability, user-friendliness, and compatibility with your SAP environment while evaluating tools.
Step 3: Design Automation Workflows
- Outline processes and specify decision points, inputs, and outputs.
Step 4: Develop and Test Bots
- To guarantee accuracy, create RPA bots with the selected tool and test them in a sandbox setting.
Step 5: Deploy and Monitor
- Introduce bots into the production environment and keep a close eye on their performance.
Step 6: Scale Automation
- If necessary, extend automation to additional SAP procedures.
Challenges in SAP RPA Implementation
1. Complex Processes
- Advanced AI skills may be needed for some SAP operations that include unstructured data or decision-making.
- Solution: For intelligent automation, combine AI and RPA.
2. Resistance to Change
- Workers may be reluctant to embrace automation because they worry about losing their jobs.
- Solution: Highlight how RPA increases productivity and supports human roles.
3. Integration Issues
- ensuring seamless SAP and other business system integration.
- Solution: Make use of RPA products and APIs certified by SAP.
4. Security and Compliance Concerns
- Strong security procedures are necessary when handling sensitive data during automation.
- Solution: Put access restriction and encryption into place.
Real-world Use Cases of RPA in SAP
Case Study 1: Automating Invoice Processing
- Problem: A retail business encountered difficulties processing invoices by hand, which resulted in mistakes and delays.
- Solution: RPA bots reduced processing time by 60% and errors by 80% by extracting, validating, and entering invoice data into SAP.
Case Study 2: Streamlining HR Operations
- Problem: Processing payroll by hand presented difficulties for a multinational company.
- Solution: RPA saved more than 200 hours per month by automating payroll computations, compliance checks, and report preparation.
Case Study 3: Sales Order Management
- Problem: Manual data entry caused delays in order processing for a manufacturing company.
- Solution: RPA increased order processing speed by 50% by automating sales order validation and updates in SAP.
Best Practices for Successful SAP RPA Implementation
Start Small
- To determine viability and improve processes, start with a pilot project.
Ensure Stakeholder Buy-in
- Early stakeholder involvement will help to allay worries and win support.
Focus on High-impact Areas
- Give top priority to automating procedures that yield the highest return on investment.
Monitor and Optimize Bots
- Evaluate bot performance on a regular basis and tweak as needed.
Invest in Employee Training
- Give staff members the tools they need to oversee and improve RPA processes.
The Future of RPA in SAP
1. Hyperautomation
- integrating analytics, AI, and machine learning with RPA to automate processes from start to finish.
2. Increased Adoption of SAP Intelligent RPA
- Because of its strong integration capabilities, SAP’s native RPA platform is anticipated to gain popularity.
3. Enhanced Cognitive Capabilities
- Because they can handle unstructured data, bots are a good fit for intricate procedures.
4. Greater Focus on Analytics
- Predictive analytics will be included into RPA technologies to provide useful information.
Conclusion
Businesses’ interactions with SAP systems are being revolutionized by robotic process automation, which offers unmatched scalability, precision, and efficiency. RPA frees up important human resources for more strategic endeavors by automating repetitive operations like data entry and report generation.
RPA technology will play a bigger part in SAP environments as it develops further, opening the door to operational excellence and intelligent automation. It is now imperative for companies looking to streamline their SAP operations to invest in RPA in order to remain competitive in the ever-changing business environment of today.
You may be interested in:
A Deep Dive into SAP API Management
Integration cloud system to HANA Cloud Platform using Cloud Connector