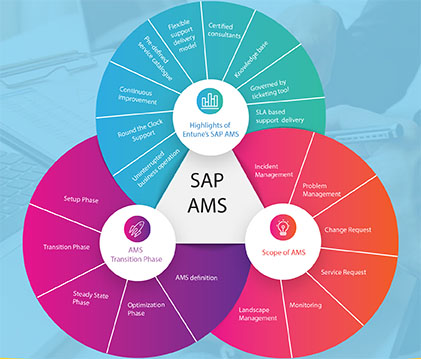
SAP implementations, while promising significant business benefits, often come with their own set of hurdles. These challenges can range from organizational resistance to technical complexities, and if not addressed effectively, can derail the entire project. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the most common challenges encountered during SAP implementations and provide practical strategies to overcome them.
Understanding the Common Challenges
Before we dive into solutions, let’s identify the most prevalent challenges that organizations face during SAP implementations:
1. Organizational Change Management
- Resistance to change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes and systems.
- Lack of user adoption: Employees may not fully utilize the system’s capabilities.
- Communication breakdown: Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings and delays.
2. Data Migration Issues
- Data quality problems: Inconsistent or inaccurate data can hinder the implementation process.
- Data mapping challenges: Identifying and mapping data between legacy systems and SAP can be complex.
- Data volume: Large volumes of data can slow down the migration process.
3. Project Scope Creep
- Unclear project objectives: Ambiguous goals can lead to scope expansion.
- Changing business requirements: Evolving business needs can impact the project timeline and budget.
- Lack of project management discipline: Poorly defined project plans can contribute to scope creep.
4. Resource Constraints
- Shortage of skilled resources: Lack of SAP expertise can delay the implementation.
- Budget limitations: Insufficient funding can impact project deliverables.
- Time constraints: Tight project deadlines can lead to rushed decisions and errors.
5. Technical Challenges
- System integration complexities: Integrating SAP with existing systems can be difficult.
- Customizations: Excessive customizations can increase project costs and complexity.
- Performance issues: System performance problems can impact user adoption and productivity.
Overcoming the Challenges
Now that we understand the common challenges, let’s explore effective strategies to overcome them:
1. Organizational Change Management
- Communicate effectively: Clearly articulate the benefits of the SAP implementation to all stakeholders.
- Involve employees: Engage employees in the change process to build ownership.
- Provide adequate training: Equip employees with the necessary skills to use the system effectively.
- Change management framework: Implement a structured change management approach.
2. Data Migration Issues
- Data quality assessment: Conduct a thorough data quality assessment to identify and address issues.
- Data cleansing: Cleanse and standardize data before migration.
- Data mapping tools: Utilize data mapping tools to automate the process.
- Data migration testing: Perform rigorous testing to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
3. Project Scope Creep
- Clear project definition: Develop a detailed project scope and obtain stakeholder approval.
- Change control process: Establish a formal process for managing changes to the project scope.
- Regular project reviews: Conduct regular project reviews to assess progress and identify potential issues.
- Risk management: Identify and mitigate project risks to prevent scope creep.
4. Resource Constraints
- Skill gap assessment: Identify skill gaps and develop a training plan.
- Outsourcing: Consider outsourcing certain tasks to supplement internal resources.
- Prioritization: Focus on critical project deliverables and prioritize tasks accordingly.
- Efficient resource utilization: Optimize resource allocation and utilization.
5. Technical Challenges
- System integration planning: Carefully plan system integrations and develop integration strategies.
- Customization guidelines: Establish clear guidelines for customizations to minimize complexity.
- Performance optimization: Monitor system performance and implement optimization measures.
- Testing and quality assurance: Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve technical issues.
Conclusion
Overcoming challenges in SAP implementations requires a combination of careful planning, effective project management, and a strong focus on change management. By addressing these challenges proactively and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, organizations can increase their chances of a successful SAP implementation.
Remember, while this guide provides valuable insights, every SAP project is unique. It’s essential to adapt these strategies to your specific circumstances and seek expert guidance when needed.
Tags: SAP implementation challenges, SAP project management, change management, data migration, SAP consulting, SAP implementation best practices, SAP project failure, SAP go-live, SAP S/4HANA, ERP implementation
5 Steps to a Smooth SAP S/4HANA Migration: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Search Intent
Before diving into the content, let’s clarify the search intent behind the keyword “5 Steps to a Successful SAP S/4HANA Migration.” Users searching for this term are likely looking for a clear, actionable roadmap to navigate the complexities of an SAP S/4HANA migration. They want practical advice, best practices, and potential pitfalls to avoid.
Step 1: Define Your Business Objectives and Scope
The foundation of a successful SAP S/4HANA migration is a clear understanding of your business goals. This step involves:
- Identifying business drivers: Pinpoint the reasons for the migration, whether it’s cost reduction, improved efficiency, enhanced customer experience, or compliance mandates.
- Defining the scope: Determine the specific modules and processes to be migrated. Consider a phased approach if the entire system migration is too complex.
- Assessing your current SAP landscape: Evaluate the health of your existing SAP system, including data quality, customizations, and integrations.
Key Considerations:
- Involve key stakeholders from different departments to ensure alignment with business objectives.
- Conduct a thorough gap analysis to identify the functionalities missing in your current system.
- Prioritize processes based on their impact on the business.
Step 2: Build a Strong Project Team
Assembling the right team is crucial for a successful migration. Consider the following roles:
- Project manager: Oversees the entire project, manages timelines, and resources.
- Business process experts: Understand the end-to-end business processes and requirements.
- SAP functional consultants: Possess deep knowledge of SAP modules and configurations.
- Technical consultants: Handle system integration, data migration, and technical aspects.
- Change management experts: Manage the impact of the migration on employees and processes.
Key Considerations:
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities within the team.
- Establish effective communication channels to facilitate collaboration.
- Provide necessary training to team members to ensure they have the required skills.
Step 3: Choose the Right Migration Approach
There are several migration approaches to choose from, each with its own advantages and challenges. The most common options include:
- Greenfield implementation: A clean slate approach, suitable for organizations with limited customizations.
- Brownfield implementation: Leveraging the existing SAP system as a starting point.
- Selective data migration: Migrating only critical data to reduce complexity and costs.
- System conversion: Converting the existing SAP system to S/4HANA.
Key Considerations:
- Evaluate the pros and cons of each approach based on your business needs and budget.
- Consider the impact of the chosen approach on data migration, customizations, and training.
- Develop a detailed migration plan outlining the steps involved.
Step 4: Data Migration and Cleansing
Data is the lifeblood of any SAP system. A robust data migration strategy is essential for a smooth transition. This step involves:
- Data assessment: Evaluate the quality, consistency, and completeness of your data.
- Data cleansing: Identify and correct data errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates.
- Data migration planning: Develop a detailed data migration plan, including data mapping and load strategies.
- Data migration testing: Perform thorough testing to ensure data integrity and accuracy.
Key Considerations:
- Use data quality tools to automate the cleansing process.
- Involve business users in data validation to ensure accuracy.
- Develop a data migration rollback plan in case of issues.
Step 5: Testing, Training, and Go-Live
The final phase involves rigorous testing, user training, and a successful go-live.
- System integration testing: Verify the integration of all SAP modules and external systems.
- User acceptance testing (UAT): Ensure the system meets business requirements and user expectations.
- End-user training: Provide comprehensive training to all users to maximize adoption.
- Change management: Support employees through the transition and address resistance to change.
- Go-live planning: Develop a detailed go-live plan, including cutover activities and post-go-live support.
Key Considerations:
- Conduct multiple rounds of testing to identify and resolve issues.
- Develop a communication plan to keep users informed about the migration progress.
- Provide ongoing support to users after the go-live to address any challenges.
Conclusion
A successful SAP S/4HANA migration requires careful planning, execution, and change management. By following these five steps and addressing the key considerations, you can increase your chances of achieving a smooth and successful transition.
Tags: SAP S/4HANA migration, SAP migration, SAP S/4HANA, SAP implementation, SAP consulting, ERP migration, digital transformation, business process optimization, data migration, change management, SAP S/4HANA training, SAP S/4HANA benefits
Optimizing Your Supply Chain with SAP SCM: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Supply Chain and its Challenges
The supply chain is the backbone of every business, encompassing the intricate network of activities involved in procuring raw materials, transforming them into finished products, and delivering them to the end customer. In today’s fast-paced, globalized economy, supply chains are facing unprecedented challenges such as:
- Increased complexity: Managing a vast network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- Demand volatility: Fluctuating customer demands making it difficult to forecast accurately.
- Global disruptions: Economic downturns, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions impacting supply chain operations.
- Supply chain visibility: Lack of real-time data and insights into supply chain activities.
To overcome these challenges and achieve operational excellence, organizations are turning to advanced supply chain management (SCM) solutions.
SAP SCM: A Powerful Tool for Supply Chain Optimization
SAP SCM is a comprehensive suite of applications designed to help businesses streamline their supply chain processes and enhance overall performance. By leveraging the capabilities of SAP SCM, organizations can:
- Improve planning and forecasting: Accurately predict demand, optimize inventory levels, and align production with market needs.
- Enhance supply chain visibility: Gain real-time insights into supply chain operations, identify potential disruptions, and proactively address issues.
- Optimize transportation and logistics: Efficiently manage transportation routes, reduce costs, and improve delivery times.
- Strengthen supplier collaboration: Improve communication and collaboration with suppliers, ensuring timely delivery of materials.
- Increase customer satisfaction: Deliver products on time, in full, and at the right cost.
Key Components of SAP SCM
SAP SCM comprises several modules that address different aspects of the supply chain:
- SAP Supply Chain Planning (SCP): Enables demand planning, production planning, and inventory optimization.
- SAP Supply Chain Execution (SCE): Manages logistics, transportation, warehouse management, and order fulfillment.
- SAP Supply Chain Collaboration (SCC): Facilitates collaboration with suppliers, customers, and partners.
- SAP Supply Chain Analytics (SCA): Provides advanced analytics capabilities to extract valuable insights from supply chain data.
Optimizing Your Supply Chain with SAP SCM
To effectively optimize your supply chain using SAP SCM, consider the following steps:
- Define Your Supply Chain Goals: Clearly articulate your supply chain objectives, such as reducing costs, improving delivery performance, or enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Conduct a Thorough Assessment: Evaluate your current supply chain processes, identify pain points, and determine areas for improvement.
- Implement SAP SCM: Choose the appropriate SAP SCM modules based on your specific requirements and integrate them with your existing systems.
- Master Data Management: Ensure accurate and up-to-date master data to support effective supply chain planning and execution.
- Leverage Advanced Planning Capabilities: Utilize SAP SCM’s advanced planning tools to optimize inventory levels, production schedules, and transportation routes.
- Improve Collaboration: Foster strong relationships with suppliers and customers through effective communication and information sharing.
- Monitor and Measure Performance: Continuously track key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess supply chain performance and identify areas for improvement.
Best Practices for SAP SCM Implementation
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Ensure buy-in from all departments involved in the supply chain.
- Change Management: Implement effective change management strategies to overcome resistance to change.
- Data Quality: Prioritize data cleansing and standardization to ensure data accuracy.
- Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training to employees on SAP SCM functionalities.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to optimize supply chain performance.
Case Study: How Company X Improved Supply Chain Efficiency with SAP SCM
[Insert a case study highlighting a company that successfully implemented SAP SCM and achieved significant improvements in supply chain performance.]
Conclusion
Optimizing your supply chain is crucial for business success. By leveraging the power of SAP SCM, organizations can enhance visibility, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver exceptional customer service. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of SAP SCM and drive your supply chain to new heights.
Tags: SAP SCM, supply chain optimization, supply chain management, SAP Supply Chain Planning, SAP Supply Chain Execution, SAP Supply Chain Collaboration, SAP Supply Chain Analytics, supply chain challenges, supply chain visibility, inventory management, transportation management, demand planning, production planning, supplier collaboration, customer satisfaction, supply chain KPIs, SAP SCM implementation, supply chain best practices
SAP for Retail: Delivering Exceptional Customer Experiences
Understanding the Retail Landscape
The retail industry is undergoing a digital transformation, driven by evolving customer expectations and technological advancements. Customers today demand personalized experiences, seamless interactions, and instant gratification. To stay competitive, retailers must leverage innovative solutions that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
SAP, a global leader in enterprise software, offers a comprehensive suite of solutions tailored to the retail industry. By implementing SAP for retail, businesses can gain a competitive edge, optimize operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
The Importance of Customer Experience in Retail
Customer experience (CX) is no longer a luxury but a necessity for retail success. Satisfied customers are more likely to make repeat purchases, recommend the brand to others, and become loyal advocates. A positive CX can drive sales, increase customer lifetime value, and build brand reputation.
SAP for retail empowers businesses to create personalized customer journeys by providing a unified view of customer data. This enables retailers to understand customer preferences, behavior, and purchase history, allowing them to offer tailored recommendations and promotions.
Key Features of SAP for Retail
SAP for retail offers a wide range of functionalities to support retail operations and enhance customer experiences. Some key features include:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manage customer interactions, track sales, and analyze customer data to gain valuable insights.
- Merchandise Management: Optimize product assortment, pricing, and promotions to maximize profitability.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Streamline supply chain operations, improve inventory management, and ensure product availability.
- Store Operations: Manage store processes, including POS, inventory, and labor management.
- E-commerce: Create engaging online shopping experiences, integrate with physical stores, and offer seamless omnichannel capabilities.
Enhancing Customer Experience with SAP for Retail
By leveraging SAP for retail, retailers can implement strategies to enhance customer experience across various touchpoints:
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: Create tailored product recommendations, personalized offers, and targeted marketing campaigns based on customer preferences and behavior.
- Omnichannel Retail: Provide a seamless shopping experience across online, mobile, and physical stores, allowing customers to shop and return products conveniently.
- Loyalty Programs: Build strong customer relationships through loyalty programs that offer rewards, exclusive benefits, and personalized offers.
- Customer Service Excellence: Empower customer service agents with the right tools and information to resolve customer issues efficiently and effectively.
- Data-Driven Insights: Utilize customer data to identify trends, preferences, and opportunities for improvement.
Success Stories and Best Practices
Many retailers have successfully implemented SAP for retail and achieved significant improvements in customer experience. By sharing success stories and best practices, we can inspire other businesses to adopt SAP and reap the benefits.
- Case Study 1: Fashion Retailer
- Implemented SAP for retail to improve inventory management, reduce stockouts, and enhance online shopping experience.
- Achieved a 20% increase in online sales and a 15% reduction in inventory holding costs.
- Case Study 2: Grocery Store Chain
- Leveraged SAP to optimize store layout, personalize promotions, and implement a loyalty program.
- Increased customer satisfaction by 15% and boosted average transaction value by 10%.
Overcoming Challenges in SAP for Retail Implementation
Implementing SAP for retail can be a complex process. However, with careful planning, execution, and support, businesses can overcome challenges and achieve successful outcomes.
- Change Management: Address employee resistance to change and provide training to ensure a smooth transition.
- Data Integration: Integrate data from various sources to create a unified view of customers and products.
- Customization: Balance the need for customization with the benefits of standard SAP functionalities.
- IT Support: Ensure adequate IT support throughout the implementation and post-implementation phases.
The Role of eLearning in Mastering SAP for Retail
To maximize the benefits of SAP for retail, organizations need skilled professionals who can effectively utilize the system. eLearning provides a flexible and accessible way to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills.
Our eLearning institute offers comprehensive SAP for retail courses designed to equip learners with the expertise to drive business success. Our courses cover various aspects of SAP for retail, including:
- SAP for retail fundamentals
- Customer relationship management
- Merchandise management
- Supply chain management
- Store operations
- E-commerce
By enrolling in our eLearning program, you will gain the skills and confidence to implement SAP for retail successfully and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Conclusion
SAP for retail is a powerful tool that can transform the way retailers interact with customers. By focusing on customer experience, leveraging SAP functionalities, and overcoming implementation challenges, businesses can achieve sustainable growth and market leadership.
Invest in your team’s SAP expertise through our eLearning program and unlock the full potential of SAP for retail.
Tags: SAP for retail, customer experience, retail industry, SAP CRM, SAP merchandise management, SAP supply chain management, SAP store operations, SAP e-commerce, eLearning, SAP training, retail technology, omnichannel retail, personalized shopping, customer loyalty, data analytics, retail best practices
Transforming the Manufacturing Industry with SAP: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Manufacturing Industry’s Challenges
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a digital revolution, driven by the need for increased efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. Traditional manufacturing processes are being disrupted by emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing. To stay ahead of the curve, manufacturers must adopt innovative solutions that can streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and enhance decision-making.
SAP, a leading provider of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, has emerged as a critical tool for manufacturers to address these challenges and drive transformation. By leveraging SAP’s comprehensive suite of solutions, manufacturers can gain a competitive edge, improve operational excellence, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
The Role of SAP in Manufacturing Transformation
SAP offers a wide range of solutions tailored to the specific needs of the manufacturing industry. These solutions cover various aspects of the manufacturing value chain, from planning and procurement to production, logistics, and customer relationship management (CRM).
1. Production Planning and Execution:
- Demand forecasting and planning: Accurately predict customer demand to optimize production schedules and inventory levels.
- Material requirements planning (MRP): Ensure the availability of necessary materials and components to meet production requirements.
- Production scheduling: Create and manage efficient production plans, considering factors such as capacity, resources, and constraints.
- Shop floor control: Monitor and control production processes in real-time, tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring quality.
2. Supply Chain Management:
- Supplier management: Build strong relationships with suppliers, optimize procurement processes, and ensure timely delivery of materials.
- Inventory management: Maintain optimal inventory levels to balance costs, customer service, and supply chain disruptions.
- Logistics and transportation: Efficiently manage the movement of goods, from raw materials to finished products.
- Supply chain visibility: Gain real-time insights into supply chain operations to improve responsiveness and reduce risks.
3. Quality Management:
- Quality planning: Define quality standards and requirements for products and processes.
- Quality control: Implement inspection and testing procedures to ensure product quality.
- Quality assurance: Monitor and improve product quality throughout the entire lifecycle.
- Quality management systems: Integrate quality management processes with other business functions.
4. Maintenance and Asset Management:
- Predictive maintenance: Use data analytics to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Asset management: Track and manage the lifecycle of assets, from acquisition to disposal.
- Work order management: Plan and execute maintenance activities efficiently.
5. Sales and Customer Relationship Management:
- Sales and order management: Process customer orders accurately and efficiently.
- Customer relationship management: Build strong customer relationships and improve customer satisfaction.
- Sales forecasting: Predict sales trends to optimize production and inventory levels.
Benefits of Implementing SAP in Manufacturing
- Increased efficiency: Streamline processes, reduce manual tasks, and improve productivity.
- Enhanced decision-making: Gain real-time insights into business operations to make informed decisions.
- Improved supply chain visibility: Optimize supply chain performance and reduce costs.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Deliver products and services on time and meet customer expectations.
- Reduced costs: Optimize resource utilization, minimize waste, and improve profitability.
- Compliance with regulations: Ensure adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Overcoming Challenges in SAP Implementation
Implementing SAP can be a complex and challenging process. To ensure successful implementation, manufacturers should consider the following:
- Change management: Address employee resistance to change and provide adequate training.
- Data migration: Migrate data accurately and efficiently from legacy systems to SAP.
- Customization: Balance the need for customization with the benefits of standard SAP functionality.
- Integration: Integrate SAP with other systems and applications to ensure seamless operations.
- Project management: Establish clear project goals, timelines, and responsibilities.
The Future of Manufacturing with SAP
The manufacturing industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer demands. SAP continues to innovate and develop new solutions to help manufacturers stay ahead of the curve. Some emerging trends in manufacturing include:
- Industry 4.0: Integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Automation of tasks and predictive analytics.
- Blockchain: Secure and transparent supply chain management.
- Additive manufacturing: Production of physical objects from digital designs.
By embracing these trends and leveraging SAP’s capabilities, manufacturers can create intelligent, connected, and sustainable operations.
Conclusion
SAP has become an indispensable tool for manufacturers seeking to transform their businesses. By implementing SAP solutions, manufacturers can improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage. While implementing SAP can be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. By carefully planning and executing the implementation process, manufacturers can reap the rewards of SAP and achieve their business goals.
Tags: SAP in manufacturing, manufacturing industry, SAP ERP, manufacturing transformation, digital manufacturing, supply chain management, production planning, quality management, maintenance management, sales and marketing, SAP implementation, Industry 4.0, AI in manufacturing, blockchain in manufacturing, additive manufacturing
SAP Solutions for the Healthcare Sector: Transforming Patient Care
The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital revolution, driven by the need for improved patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. SAP, a global leader in enterprise software, offers a comprehensive suite of solutions tailored to address the unique challenges faced by healthcare organizations. In this blog, we will explore how SAP solutions can transform the healthcare sector, from patient care to financial management.
Understanding the Healthcare Industry’s Challenges
Before diving into SAP solutions, it’s essential to understand the key challenges faced by healthcare providers:
- Rising healthcare costs: The ever-increasing cost of medical care is a major concern for both patients and healthcare organizations.
- Complex regulatory environment: Healthcare providers must comply with a myriad of regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, which can be burdensome.
- Patient safety: Ensuring patient safety is paramount, and healthcare organizations must implement robust systems to prevent medical errors.
- Data management: The volume of patient data is growing exponentially, making it challenging to manage and analyze information effectively.
- Interoperability: Seamlessly sharing patient information between different healthcare systems is crucial for providing coordinated care.
How SAP Solutions Address Healthcare Challenges
SAP offers a range of solutions that can help healthcare organizations overcome these challenges and achieve their goals.
1. SAP S/4HANA for Healthcare
SAP S/4HANA is a comprehensive ERP solution that provides a solid foundation for digital transformation in healthcare. It offers a unified platform for managing core business processes, including finance, supply chain, and human resources. Key benefits of SAP S/4HANA for healthcare include:
- Real-time insights: Access to real-time data enables better decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
- Financial management: Streamline financial processes, including revenue cycle management and cost accounting.
- Supply chain optimization: Manage inventory levels effectively and reduce supply chain costs.
- Patient engagement: Enhance patient experience through personalized communication and self-service portals.
2. SAP Healthcare Analytics
Data-driven insights are essential for improving patient care and organizational performance. SAP Healthcare Analytics provides advanced analytics capabilities to help healthcare organizations uncover valuable information from their data. Key features include:
- Predictive analytics: Identify potential risks and opportunities to improve patient outcomes.
- Population health management: Analyze patient populations to identify trends and develop targeted interventions.
- Financial performance management: Gain insights into financial performance and identify cost-saving opportunities.
3. SAP SuccessFactors for Healthcare
Attracting and retaining top talent is crucial in the healthcare industry. SAP SuccessFactors offers a comprehensive human capital management solution to help healthcare organizations optimize their workforce. Key benefits include:
- Talent management: Identify, develop, and retain high-performing employees.
- Employee engagement: Improve employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Compliance management: Ensure adherence to healthcare regulations.
4. SAP Ariba for Healthcare
Efficient procurement is essential for controlling costs and ensuring the availability of medical supplies. SAP Ariba provides a cloud-based procurement platform that helps healthcare organizations streamline their procurement processes. Key features include:
- Supplier management: Manage relationships with suppliers and improve collaboration.
- Spend analysis: Identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize spending.
- Contract management: Manage contracts effectively to reduce costs and risks.
The Role of SAP in Improving Patient Care
By leveraging SAP solutions, healthcare organizations can significantly improve patient care by:
- Enhancing patient experience: Providing personalized care, improving communication, and streamlining administrative processes.
- Improving patient safety: Reducing medical errors through better data management and process automation.
- Increasing efficiency: Optimizing operations and reducing costs to reinvest in patient care.
- Supporting population health management: Identifying and addressing the needs of specific patient populations.
Conclusion
SAP offers a comprehensive suite of solutions that can help healthcare organizations address their most pressing challenges and achieve their goals. By embracing digital transformation and leveraging the power of SAP, healthcare providers can deliver better patient care, improve operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
Tags: SAP Healthcare, SAP S/4HANA Healthcare, SAP Healthcare Analytics, SAP SuccessFactors Healthcare, SAP Ariba Healthcare, healthcare IT, healthcare solutions, healthcare management, patient care, healthcare industry, digital healthcare
Why SAP Managed Services Are Essential for Business Growth
Understanding the SAP Landscape
SAP, a behemoth in enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, is a cornerstone for many businesses. Its intricate functionalities, from finance and HR to supply chain and customer relationship management, offer unparalleled efficiency and insights. However, managing such a complex system requires specialized expertise, which is where SAP managed services come into play.
The Challenges of Managing SAP In-House
While many organizations initially opt for in-house SAP management, the complexities and resource demands often lead to challenges.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: Finding, hiring, and retaining skilled SAP professionals is a persistent challenge.
- Cost Overruns: Unexpected system issues, upgrades, and customizations can lead to escalating costs.
- System Downtime: Technical glitches or human errors can result in costly system downtime.
- Focus Diversion: Internal IT teams may be pulled away from strategic initiatives to manage day-to-day SAP operations.
- Compliance Risks: Staying updated with SAP regulations and security best practices is time-consuming and complex.
The SAP Managed Services Advantage
SAP managed services offer a comprehensive solution to these challenges by providing specialized expertise and resources.
- Deep SAP Expertise: Managed service providers have a deep understanding of SAP systems, enabling them to optimize performance and address issues promptly.
- Cost Efficiency: By outsourcing SAP management, organizations can reduce operational costs and focus on core business activities.
- Risk Mitigation: Managed service providers implement robust security measures and stay updated with compliance regulations.
- Scalability: They can easily adapt to changing business needs, scaling resources up or down as required.
- Innovation Focus: With SAP management handled by experts, internal IT teams can concentrate on strategic initiatives and digital transformation.
Key Benefits of SAP Managed Services
- Improved System Performance: Managed service providers optimize SAP systems for peak performance, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
- Enhanced Security: Robust security measures protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Managed service providers accelerate SAP implementations and upgrades.
- Reduced Costs: By streamlining operations and eliminating inefficiencies, managed services can significantly reduce IT expenses.
- Access to Expertise: Tap into a pool of SAP experts for specialized knowledge and support.
Choosing the Right SAP Managed Service Provider
Selecting the right partner is crucial for the success of your SAP managed services. Consider the following factors:
- Expertise and Experience: Look for a provider with a proven track record in SAP management.
- Service Offerings: Ensure the provider offers the services your organization needs, such as application management, infrastructure management, and cloud migration.
- Customer References: Check the provider’s reputation and client testimonials.
- Pricing and Contracts: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the service and understand the contract terms.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations cannot afford to be bogged down by the complexities of SAP management. By partnering with a reputable SAP managed service provider, businesses can unlock the full potential of their SAP investment, drive growth, and focus on core competencies.
Tags: SAP managed services, SAP consulting, business growth, IT outsourcing, SAP support, SAP optimization, SAP cloud, SAP migration, ERP management, IT services.
The Benefits of Outsourcing Your SAP Support: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
SAP, a complex enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, is critical to the operations of many businesses. Managing SAP effectively requires specialized expertise, resources, and time. Outsourcing your SAP support can offer several benefits, from cost savings to improved efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the advantages of outsourcing SAP support in detail.
Core Benefits of Outsourcing SAP Support
Cost Savings
- Reduced labor costs: Outsourcing allows you to eliminate the overhead associated with hiring and maintaining an in-house SAP support team.
- Optimized resource allocation: Focus your internal resources on core business functions while external experts handle SAP support.
- Predictable costs: Many outsourcing providers offer fixed-fee contracts, providing budget certainty.
Improved Efficiency
- Faster response times: Outsourcing often results in quicker issue resolution due to specialized expertise and dedicated support teams.
- Increased productivity: Free up internal resources to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine SAP tasks.
- Access to specialized skills: Outsourcing provides access to a pool of SAP experts with diverse skill sets.
Enhanced Focus on Core Business
- Strategic alignment: By outsourcing SAP support, you can concentrate on core business objectives and growth strategies.
- Improved decision-making: Reduced operational burdens allow for more strategic thinking and better decision-making.
- Agility and adaptability: Outsourcing enables you to quickly adapt to changing business needs and market conditions.
Risk Mitigation
- Reduced downtime: Outsourcing can minimize system downtime and disruptions through proactive monitoring and maintenance.
- Compliance adherence: Outsourcing providers often have deep expertise in industry regulations and compliance requirements.
- Disaster recovery planning: Many outsourcing providers offer robust disaster recovery plans to protect your SAP environment.
Access to Expertise and Technology
- Specialized knowledge: Outsourcing provides access to SAP experts with in-depth knowledge of the latest trends and best practices.
- Advanced technologies: Outsourcing providers often invest in cutting-edge technologies and tools to improve SAP support efficiency.
- Continuous improvement: Outsourcing partners are committed to staying updated with SAP advancements and industry best practices.
How to Choose the Right Outsourcing Partner
Selecting the right SAP support outsourcing partner is crucial for realizing the benefits outlined above. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Expertise and experience: Look for a provider with a proven track record in SAP support and your industry.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Ensure the provider offers clear SLAs for response times, resolution times, and uptime guarantees.
- Security and compliance: Verify the provider’s security measures and adherence to industry regulations.
- Cost structure: Evaluate different pricing models and choose the one that aligns with your budget and requirements.
- References and case studies: Check the provider’s reputation and customer testimonials.
Conclusion
Outsourcing your SAP support can yield significant benefits for your organization, including cost savings, improved efficiency, enhanced focus on core business, risk mitigation, and access to expertise and technology. By carefully selecting the right outsourcing partner, you can optimize your SAP investment and drive business growth.
Tags: SAP support outsourcing, benefits of outsourcing SAP, SAP outsourcing, SAP support services, SAP managed services, SAP consulting, IT outsourcing, cost savings, efficiency, risk mitigation, expertise
How Managed Services Can Supercharge Your SAP ROI
Understanding the Challenge
SAP, a behemoth of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, offers unparalleled capabilities for businesses. However, harnessing its full potential often requires specialized expertise, substantial resources, and ongoing maintenance. This is where SAP Managed Services come into play.
What is SAP Managed Services?
SAP Managed Services is a comprehensive solution that outsources the management, maintenance, and support of your SAP systems to a third-party provider. This allows your organization to focus on core business activities while the service provider ensures optimal performance, security, and compliance.
The Importance of Maximizing SAP ROI
SAP is a significant investment. To justify the expenditure, businesses must extract maximum value from their SAP systems. This is where ROI, or Return on Investment, becomes a critical metric. A high SAP ROI indicates that the system is generating substantial benefits relative to its cost.
How Managed Services Boost SAP ROI
- Cost Reduction:
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Managed service providers have specialized teams and tools to efficiently manage SAP systems, reducing the need for in-house resources.
- Reduced Hardware and Software Costs: By leveraging economies of scale, managed service providers can offer cost-effective hardware and software solutions.
- Predictable Expenses: Managed service contracts often include fixed fees, providing better budgeting and financial planning.
- Enhanced System Performance:
- Proactive Monitoring: Managed service providers continuously monitor SAP systems to identify and address potential issues before they impact operations.
- Performance Tuning: Experts optimize system performance to ensure optimal speed and responsiveness.
- Regular Upgrades and Patches: Managed service providers keep SAP systems up-to-date with the latest patches and upgrades, preventing vulnerabilities and enhancing functionality.
- Improved System Availability:
- 24/7 Support: Managed service providers offer round-the-clock support to minimize system downtime.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Comprehensive disaster recovery plans ensure business continuity in case of unforeseen events.
- Increased Productivity:
- Focus on Core Competencies: By offloading SAP management, internal teams can concentrate on strategic initiatives that drive business growth.
- Faster Issue Resolution: Managed service providers have experienced teams that can quickly diagnose and resolve issues.
- Risk Mitigation:
- Security Compliance: Managed service providers adhere to strict security standards, protecting sensitive data.
- Audit Support: They assist with audits and compliance requirements.
Selecting the Right Managed Service Provider
Choosing the right managed service provider is crucial for maximizing SAP ROI. Consider the following factors:
- Expertise: Look for a provider with a proven track record in SAP management.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Ensure the provider offers robust SLAs for uptime, response times, and resolution times.
- Security Measures: Verify the provider’s security certifications and practices.
- Pricing Model: Evaluate different pricing models (fixed fee, usage-based, etc.) to find the best fit for your budget.
- References: Check customer references to assess the provider’s performance.
Conclusion
Implementing SAP Managed Services is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance your SAP ROI. By reducing costs, improving performance, increasing productivity, and mitigating risks, managed services empower businesses to focus on their core competencies and achieve greater success.
Tags: SAP Managed Services, SAP ROI, SAP Consulting, SAP Support, SAP Optimization, IT Outsourcing, ERP Management, Cloud Computing, Digital Transformation, Business Efficiency
Leveraging SAP HANA for Advanced Analytics: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Power of SAP HANA for Advanced Analytics
SAP HANA, an in-memory database platform, has revolutionized the way businesses handle data. Its ability to process vast amounts of data at lightning speed has made it a cornerstone for advanced analytics. But what does this mean for businesses?
What is Advanced Analytics?
Before diving into SAP HANA, it’s essential to understand advanced analytics. This is a broad term encompassing a variety of techniques used to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations in data. It goes beyond traditional reporting and business intelligence (BI) by delving deeper into the data to predict future outcomes and optimize business decisions.
Why SAP HANA for Advanced Analytics?
- Speed: HANA’s in-memory computing eliminates the need for data to be moved between storage and processing, significantly accelerating query performance.
- Scalability: It can handle massive datasets and complex analytics workloads, growing with your business needs.
- Integration: HANA seamlessly integrates with other SAP applications, providing a unified platform for data management and analysis.
- Advanced Features: It offers built-in analytics functions, predictive modeling, and text mining capabilities.
Core Components of SAP HANA for Advanced Analytics
To leverage SAP HANA effectively, it’s crucial to understand its core components:
- SAP HANA Database: The foundation, providing in-memory storage and processing.
- SAP HANA Analytics Platform: A suite of tools for data modeling, analysis, and visualization.
- SAP HANA Predictive Analytics: For building predictive models and forecasting.
- SAP HANA Text Analysis: For extracting insights from unstructured text data.
Real-World Applications of SAP HANA for Advanced Analytics
The applications of SAP HANA are vast and varied. Here are some examples:
- Customer Analytics: Identify high-value customers, predict churn, and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Fraud Detection: Detect fraudulent transactions in real-time using anomaly detection.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Optimize inventory levels, improve demand forecasting, and streamline logistics.
- Risk Management: Assess financial risks and optimize investment portfolios.
- Precision Marketing: Create targeted marketing campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences.
Building a Robust Analytics Foundation with SAP HANA
To maximize the benefits of SAP HANA, follow these steps:
- Data Quality: Ensure data accuracy and consistency for reliable insights.
- Data Modeling: Create efficient data models to support analytics queries.
- Performance Optimization: Fine-tune HANA for optimal performance.
- User Adoption: Train users to effectively utilize HANA’s capabilities.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor analytics performance and refine models over time.
Overcoming Challenges in SAP HANA Implementation
Implementing SAP HANA can present challenges. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- Data Volume: For massive datasets, consider data partitioning and compression.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Identify performance bottlenecks and optimize accordingly.
- Skill Gap: Invest in training for your analytics team.
- Integration: Ensure seamless integration with existing systems.
The Future of SAP HANA in Advanced Analytics
SAP HANA continues to evolve with advancements in technology. Look forward to:
- Cloud-based HANA: Increased flexibility and scalability.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Deeper insights and automation.
- IoT Integration: Real-time analytics on sensor data.
Conclusion
SAP HANA is a powerful tool for driving business growth through advanced analytics. By understanding its capabilities and best practices, organizations can unlock valuable insights and gain a competitive edge.
Remember: This is just the tip of the iceberg. To truly master SAP HANA, consider enrolling in a comprehensive eLearning course that delves deeper into its intricacies and practical applications.
Tags: SAP HANA, advanced analytics, data analytics, business intelligence, in-memory database, data warehousing, big data, data science, predictive analytics, data mining, data visualization, SAP HANA tutorials, SAP HANA training, SAP HANA certification
Best Practices for SAP Cloud Platform Development: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the SAP Cloud Platform
Before delving into best practices, it’s essential to grasp the SAP Cloud Platform (SCP). It’s a robust platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering from SAP, enabling developers to build, deploy, and run cloud applications. The platform provides a wide range of services, including integration, data management, analytics, and application development.
Core Principles for SAP Cloud Platform Development
- Design for Scalability:
- Anticipate future growth: Design applications to handle increasing loads without compromising performance.
- Leverage SCP’s scaling capabilities: Utilize services like Cloud Foundry to automatically scale applications based on demand.
- Optimize resource utilization: Efficiently use CPU, memory, and storage to reduce costs.
- Security First:
- Follow security best practices: Implement strong authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
- Leverage SCP’s security features: Utilize services like Identity Authentication and Cloud Identity Services.
- Conduct regular security audits: Identify and address vulnerabilities promptly.
- Performance Optimization:
- Profile and optimize code: Identify performance bottlenecks and optimize accordingly.
- Utilize caching: Store frequently accessed data in memory to improve response times.
- Leverage asynchronous processing: Offload heavy tasks to background jobs.
- Cost Optimization:
- Right-size resources: Allocate resources based on actual usage.
- Monitor resource consumption: Identify opportunities to reduce costs.
- Leverage cost-saving features: Take advantage of SCP’s pricing models and discounts.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
- Automate the build, test, and deployment process: Improve efficiency and reduce errors.
- Use DevOps practices: Foster collaboration between development and operations teams.
- Implement version control: Track code changes and enable rollbacks.
- API-Led Development:
- Design reusable APIs: Create well-defined interfaces for application components.
- Leverage API management: Secure and manage APIs effectively.
- Adopt a microservices architecture: Build loosely coupled, independently deployable services.
- User Experience (UX) Design:
- Focus on user needs: Create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
- Follow design guidelines: Adhere to SAP Fiori design principles.
- Test with real users: Gather feedback and iterate on the design.
- Error Handling and Logging:
- Implement robust error handling: Gracefully handle exceptions and provide informative messages.
- Utilize centralized logging: Collect and analyze logs for troubleshooting and monitoring.
- Set up alerts: Notify relevant teams of critical issues.
- Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Write comprehensive unit tests: Ensure code quality and reliability.
- Conduct integration testing: Verify interactions between components.
- Perform performance testing: Assess application performance under load.
- Monitoring and Optimization:
- Use monitoring tools: Track application performance and resource utilization.
- Analyze logs: Identify performance bottlenecks and issues.
- Continuously optimize: Make data-driven improvements.
Additional Best Practices
- Leverage SCP Services: Explore and utilize the full range of SCP services to enhance your applications.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest SCP features and best practices.
- Follow Coding Standards: Adhere to consistent coding conventions for maintainability.
- Document Your Code: Write clear and concise comments to improve code readability.
- Collaborate with Other Teams: Work closely with business analysts, UX designers, and QA engineers.
Conclusion
By following these best practices, you can build high-quality, scalable, and secure SAP Cloud Platform applications. Remember that development is an iterative process, so continuously evaluate and refine your approach based on feedback and performance metrics.
Tags: SAP Cloud Platform, SAP Cloud Platform Development, SCP Best Practices, Cloud Development, SAP Development, PaaS Development, SAP Fiori, Cloud Foundry, API Development, Microservices, DevOps, CI/CD, Performance Optimization, Security, Scalability, User Experience, Error Handling, Logging, Monitoring
AI and Machine Learning in SAP: A Practical Guide
Understanding the Convergence of AI and SAP
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into SAP systems is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. This powerful combination unlocks unprecedented insights, automates processes, and drives innovation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of AI and ML, their applications within the SAP ecosystem, and practical steps to harness their potential.
What is AI and Machine Learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. It involves tasks such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, language understanding, and the ability to move and manipulate objects.
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms build a mathematical model based on sample data, known as “training data,” in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to perform the task.
The Role of AI and ML in SAP
SAP, a leading enterprise software provider, has embraced AI and ML to enhance its solutions and deliver greater value to customers. Here are some key areas where AI and ML are making a significant impact:
Predictive Analytics
- Demand Forecasting: Accurately predicting customer demand for products and services.
- Fraud Detection: Identifying fraudulent activities in real-time.
- Customer Churn Prediction: Anticipating customer attrition to implement retention strategies.
Process Automation
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automating repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and accuracy.
- Intelligent Automation: Combining RPA with AI for complex decision-making processes.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Enhancing customer service and support.
Decision Support
- Prescriptive Analytics: Recommending optimal actions based on data-driven insights.
- Personalized Recommendations: Offering tailored product suggestions to customers.
- Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating potential risks.
Data Management
- Data Quality Improvement: Identifying and correcting data inconsistencies.
- Master Data Management: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency across systems.
- Data Governance: Implementing data policies and standards.
Practical Steps to Implement AI and ML in SAP
- Identify Business Problems: Clearly define the business challenges that can be addressed with AI and ML.
- Data Preparation: Collect, clean, and prepare relevant data for analysis.
- Model Development: Build and train ML models using appropriate algorithms.
- Model Deployment: Integrate the ML models into SAP systems for real-time decision-making.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor model performance and make necessary adjustments.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy and completeness is crucial for successful AI and ML implementations.
- Talent Acquisition: Finding skilled AI and ML professionals can be challenging.
- Ethical Considerations: Addressing biases and privacy concerns is essential.
Conclusion
AI and ML are transforming the SAP landscape, offering immense opportunities for businesses to gain a competitive edge. By understanding the fundamentals, exploring practical applications, and addressing challenges, organizations can successfully leverage these technologies to drive innovation and achieve their strategic goals.
Tags:
AI and Machine Learning in SAP, SAP AI, SAP ML, AI in SAP, Machine Learning in SAP, SAP Analytics, Predictive Analytics with SAP, SAP Process Automation, SAP RPA, SAP Chatbot, SAP Virtual Assistant, SAP Data Management, AI and ML in Business, AI and ML for Enterprise, SAP AI and ML Tutorial, SAP AI and ML Course, AI and ML in Supply Chain, AI and ML in Finance, AI and ML in HR, AI and ML in Sales, AI and ML in Marketing, AI and ML Trends, AI and ML Future
Advanced Managed Services for the Financial Services Industry: A Deep Dive
Understanding the Need for Advanced Managed Services in Financial Services
The financial services industry is a complex ecosystem characterized by stringent regulations, intense competition, and the ever-evolving customer expectations. To thrive in this dynamic landscape, financial institutions must prioritize operational efficiency, risk management, and customer experience. This is where advanced managed services come into play.
What are Advanced Managed Services?
Advanced managed services go beyond traditional IT support. They encompass a comprehensive suite of IT services, leveraging cutting-edge technologies and industry best practices to optimize business operations. In the context of financial services, these services are tailored to address the unique challenges of the sector, such as data security, compliance, and real-time transaction processing.
Key Benefits of Advanced Managed Services for Financial Institutions
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By streamlining IT operations and automating routine tasks, financial institutions can achieve significant cost savings and improve productivity.
- Improved Risk Management: Advanced managed service providers offer robust security measures and compliance frameworks to protect sensitive financial data and mitigate risks.
- Accelerated Digital Transformation: These services provide the necessary infrastructure and expertise to support innovation and digital initiatives.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Financial institutions can adapt to changing business needs and market conditions with ease.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing non-core IT functions, financial institutions can concentrate on their core business activities.
Core Components of Advanced Managed Services for Financial Services
To deliver maximum value, advanced managed services for the financial services industry typically include the following components:
- IT Infrastructure Management: This encompasses the management of hardware, software, and networks to ensure optimal performance and availability.
- Cloud Services: Leveraging cloud technologies can provide scalability, cost-efficiency, and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting sensitive financial data from cyber threats is paramount. Advanced managed services include robust security measures such as threat detection, incident response, and data encryption.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Staying compliant with industry regulations is crucial. Managed service providers offer expertise in navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
- Data Management and Analytics: Effective data management and advanced analytics can drive business insights and inform decision-making.
- Application Management: Ensuring the smooth operation of critical applications is essential for business continuity.
Selecting the Right Advanced Managed Service Provider
Choosing the right partner is critical for the success of your managed services initiative. Consider the following factors when selecting a provider:
- Industry Experience: Look for a provider with a proven track record in the financial services industry.
- Technical Expertise: The provider should possess deep knowledge of relevant technologies and platforms.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that the provider has robust security measures and a strong compliance record.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Clearly defined SLAs guarantee service quality and uptime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the overall cost of ownership, including pricing models and potential hidden costs.
The Future of Advanced Managed Services in Financial Services
The financial services industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by factors such as digitalization, AI, and blockchain. Advanced managed services will continue to evolve to address these emerging trends. Some key areas of focus include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Leveraging AI and ML to enhance fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer experience.
- Blockchain Technology: Exploring the potential of blockchain for secure and transparent transactions.
- Data Privacy and Protection: Strengthening data protection measures in response to evolving regulations.
- Hybrid Cloud Environments: Managing complex IT infrastructures that combine on-premises and cloud resources.
By embracing advanced managed services, financial institutions can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive market.
Tags: Advanced Managed Services, Financial Services, IT Managed Services, Cloud Services, Cybersecurity, Compliance, Data Management, Digital Transformation, Financial Technology, IT Outsourcing, Managed Service Provider, MSP
Optimizing SAP for the Automotive Sector: A Comprehensive Guide
The automotive industry is a complex ecosystem characterized by rapid technological advancements, stringent regulations, and intense competition. To thrive in this dynamic landscape, automotive companies must leverage advanced technologies to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation. SAP, a leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution, offers a robust platform to address these challenges. This blog delves into the intricacies of optimizing SAP for the automotive sector, exploring key areas, best practices, and the potential benefits.
Understanding the Automotive Industry’s Unique Challenges
Before diving into SAP optimization, it’s crucial to comprehend the specific challenges faced by automotive companies:
- Complex supply chain management: Managing a vast network of suppliers, dealers, and logistics providers is critical.
- Product lifecycle management (PLM): Efficiently managing product development, engineering, and manufacturing processes is essential.
- Quality control and compliance: Adhering to stringent quality standards and regulatory requirements is paramount.
- Sales and distribution: Managing a diverse customer base and dealer network effectively is vital.
- After-sales service: Providing excellent customer support and managing warranty claims efficiently is crucial.
The Role of SAP in the Automotive Industry
SAP offers a comprehensive suite of solutions tailored to the automotive industry, including:
- SAP S/4HANA: Provides a digital core for real-time insights and decision-making.
- SAP Supply Chain Management (SCM): Optimizes supply chain visibility and collaboration.
- SAP Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Manages product development from concept to retirement.
- SAP Customer Experience (CX): Enhances customer interactions and loyalty.
- SAP Automotive Industry Solutions: Provides industry-specific functionalities and best practices.
Key Areas for SAP Optimization in the Automotive Sector
To maximize the value of SAP, automotive companies should focus on the following areas:
1. Supply Chain Optimization
- Demand planning and forecasting: Accurately predicting customer demand to optimize inventory levels and production planning.
- Supplier collaboration: Enhancing collaboration with suppliers to improve supply chain visibility and responsiveness.
- Transportation management: Optimizing transportation routes and modes to reduce costs and improve delivery times.
- Inventory management: Implementing effective inventory control strategies to minimize stockouts and excess inventory.
2. Production Planning and Execution
- Production scheduling: Optimizing production schedules to meet customer demand while maximizing resource utilization.
- Quality management: Integrating quality control processes into the production process to ensure product excellence.
- Lean manufacturing: Implementing lean principles to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
- Production planning and control: Effectively managing production processes from planning to execution.
3. Sales and Distribution
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Building strong customer relationships and providing personalized experiences.
- Sales force automation: Empowering sales teams with tools to increase productivity and sales.
- Order management: Streamlining order processing and fulfillment to improve customer satisfaction.
- Dealer management: Effective collaboration with dealers to enhance sales performance.
4. Finance and Accounting
- Financial closing: Accelerating financial closing processes to improve financial reporting.
- Cost management: Analyzing costs and identifying opportunities for cost reduction.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks.
- Compliance: Adhering to financial regulations and reporting requirements.
5. Service and Maintenance
- Service management: Efficiently managing service requests and providing timely support.
- Warranty management: Streamlining warranty claims processing and reducing costs.
- Spare parts management: Optimizing spare parts inventory and availability.
- Field service management: Enhancing field service operations for improved customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for SAP Optimization
- Data quality: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency is crucial for successful SAP implementation.
- User adoption: Providing comprehensive training and support to encourage user adoption.
- Change management: Effectively managing organizational change to facilitate SAP implementation.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly evaluating SAP performance and identifying opportunities for improvement.
- Integration: Integrating SAP with other systems to create a seamless business process.
- Cloud adoption: Considering the benefits of cloud-based SAP solutions for scalability and flexibility.
Benefits of Optimizing SAP for the Automotive Sector
By optimizing SAP, automotive companies can achieve the following benefits:
- Improved operational efficiency
- Enhanced supply chain visibility
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Reduced costs
- Accelerated time-to-market
- Better decision-making
- Compliance with industry regulations
Conclusion
Optimizing SAP for the automotive sector is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in this competitive industry. By focusing on key areas, implementing best practices, and leveraging the full potential of SAP, automotive companies can gain a significant competitive advantage.
Tags: SAP optimization, automotive industry, supply chain management, production planning, sales and distribution, finance and accounting, service and maintenance, SAP S/4HANA, SAP SCM, SAP PLM, SAP CX, SAP Automotive Industry Solutions, ERP, digital transformation, industry 4.0, automotive technology
Tips for Building Custom SAP Applications: A Comprehensive Guide
Building custom SAP applications can be a complex and challenging task, but it can also be incredibly rewarding. With the right approach, you can create applications that meet the specific needs of your business and improve efficiency and productivity.
In this blog post, we will provide you with some tips for building custom SAP applications. We will cover everything from planning and design to development and testing.
Understanding the Basics
Before you start building a custom SAP application, it is important to have a solid understanding of the SAP platform. This includes the following:
- SAP ABAP: The core programming language for SAP applications.
- SAP UI5: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
- SAP Fiori: A design language for SAP applications.
- SAP NetWeaver: The underlying platform for SAP applications.
Once you have a good understanding of these basics, you can start planning and designing your custom application.
Planning and Design
The planning and design phase is crucial for the success of any custom SAP application. During this phase, you will define the scope of your application, identify the target users, and create a detailed design document.
Some key tips for planning and designing your custom SAP application include:
- Define the scope of your application: What are the specific business needs that your application will address?
- Identify the target users: Who will be using the application? What are their needs and expectations?
- Create a detailed design document: This document should outline the functionality of the application, the user interface, and the data model.
- Involve key stakeholders: Get input from all relevant stakeholders, including business users, IT professionals, and developers.
Development
Once you have a clear plan for your custom SAP application, you can start the development process. This involves writing the code, testing the application, and deploying it to production.
Some key tips for developing your custom SAP application include:
- Follow best practices: Use coding standards and best practices to ensure the quality of your code.
- Test thoroughly: Test your application thoroughly to identify and fix bugs.
- Use version control: Use a version control system to track changes to your code.
- Document your code: Write clear and concise comments in your code to help others understand it.
Testing
Testing is an essential part of the development process. It helps to ensure that your custom SAP application meets the requirements and works as expected.
There are different types of testing that you can perform, including:
- Unit testing: Test individual units of code.
- Integration testing: Test how different parts of the application work together.
- System testing: Test the entire application in a simulated production environment.
- User acceptance testing: Get feedback from end users to ensure that the application meets their needs.
Deployment
Once your custom SAP application has been tested and approved, you can deploy it to production. This involves moving the application to the production environment and making it available to users.
Some key tips for deploying your custom SAP application include:
- Create a deployment plan: Outline the steps involved in deploying the application.
- Perform backups: Create backups of your application and data before deployment.
- Monitor performance: Monitor the performance of the application in production.
- Provide support: Provide support to users of the application.
Additional Tips
In addition to the tips mentioned above, here are some additional tips for building custom SAP applications:
- Use a phased approach: Break down the development process into smaller phases to manage complexity.
- Leverage existing components: Reuse existing SAP components whenever possible to save time and effort.
- Consider cloud-based options: Explore cloud-based SAP options to reduce infrastructure costs.
- Stay up-to-date with SAP technology: Keep up with the latest SAP trends and technologies.
By following these tips, you can build high-quality custom SAP applications that meet the needs of your business.
Tags: custom SAP application development, SAP ABAP, SAP UI5, SAP Fiori, SAP NetWeaver, SAP application development best practices, SAP application development tips, SAP application development tutorial, SAP application development guide, SAP application development process, SAP application development methodology
Best Practices for SAP ABAP Development: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Importance of ABAP Development Best Practices
SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) is the cornerstone of SAP systems. It’s the language used to develop, customize, and maintain SAP applications. Writing efficient, maintainable, and secure ABAP code is crucial for the overall performance and stability of an SAP system. Adhering to best practices is not just a recommendation; it’s a necessity.
Foundational Best Practices
Code Readability and Maintainability
- Meaningful Naming Conventions: Use clear and descriptive names for variables, constants, and data types. Avoid cryptic abbreviations.
- Consistent Formatting: Employ consistent indentation, spacing, and code layout for enhanced readability.
- Comments: Provide clear and concise comments to explain complex logic or code sections.
- Modularity: Break down code into smaller, reusable modules or functions.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Leverage OOP concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism for better code structure.
Performance Optimization
- Database Access Optimization: Minimize database round trips, use efficient SELECT statements, and consider indexing.
- Internal Tables: Optimize internal table handling by using appropriate work areas and header lines.
- Performance-Aware Coding: Profile code to identify performance bottlenecks and apply optimizations.
- Data Dictionary Optimization: Ensure data types and structures are optimized for performance.
Error Handling and Debugging
- Exception Handling: Implement robust error handling mechanisms to prevent system crashes.
- Debugging Tools: Utilize debugging tools effectively to identify and fix issues.
- Unit Testing: Write comprehensive unit tests to ensure code quality and prevent regressions.
Security
- Authorization Checks: Implement proper authorization checks to protect sensitive data.
- Input Validation: Validate user input to prevent security vulnerabilities.
- Secure Coding Practices: Adhere to secure coding standards to mitigate risks.
Advanced Best Practices
ABAP Objects
- Encapsulation: Protect data integrity by encapsulating data and methods within classes.
- Inheritance: Create class hierarchies to promote code reuse and maintainability.
- Polymorphism: Enable flexible code design through polymorphism.
Performance Tuning
- SQL Performance Tuning: Optimize database queries using indexes, joins, and SQL tuning techniques.
- ABAP Memory Management: Manage memory efficiently to avoid performance issues.
- Batch Jobs: Schedule resource-intensive tasks for off-peak hours.
SAP HANA Integration
- AMDP (ABAP Managed Database Procedures): Leverage AMDP for performance-critical calculations.
- CDS (Core Data Services): Use CDS views for efficient data access.
- HANA-Optimized ABAP: Write ABAP code that takes advantage of HANA’s in-memory capabilities.
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): Write tests before writing code.
- Code Reviews: Conduct regular code reviews to improve code quality.
- Static Code Analysis: Use static code analysis tools to identify potential issues.
Best Practices for Specific ABAP Areas
Reports
- Performance Optimization: Use ALV Grid Control for efficient data display.
- User Interface: Design user-friendly reports with clear layouts and filters.
Dialog Programming
- Screen Design: Create intuitive and visually appealing screens.
- PBO and PAI: Understand the PBO and PAI modules for screen processing.
- Dynpros: Use dynamic programming for flexible screen layouts.
Function Modules
- Modularity: Create reusable function modules with clear interfaces.
- Performance: Optimize function module performance by avoiding unnecessary database accesses.
- Error Handling: Implement proper error handling mechanisms.
BAPIs
- Consistency: Adhere to BAPI standards for data consistency.
- Performance: Optimize BAPI performance for efficient data transfer.
- Error Handling: Handle errors gracefully to provide meaningful messages.
Continuous Improvement
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest ABAP developments and best practices.
- Learn from Others: Share knowledge and learn from experienced ABAP developers.
- Code Refactoring: Regularly review and improve existing code.
Conclusion
By following these best practices, you can significantly enhance the quality, efficiency, and maintainability of your ABAP code. Remember, mastering ABAP development is an ongoing journey. Continuous learning and improvement are essential for staying ahead in the SAP landscape.
Tags: SAP ABAP, ABAP Development, ABAP Best Practices, SAP ABAP Programming, ABAP Coding Standards, ABAP Performance, ABAP Security, ABAP OOP, ABAP Development Tips, SAP ABAP Tutorial, ABAP Development Guidelines
Introduction to SAP UI5 Development: Your Comprehensive Guide
Understanding SAP UI5
SAP UI5, short for SAP User Interface for HTML5, is a JavaScript library used to build responsive web applications that integrate seamlessly with SAP backend systems. It offers a rich set of controls, data binding capabilities, and routing functionalities, making it a preferred choice for developers creating modern and engaging user interfaces for SAP applications.
Why Learn SAP UI5?
The demand for SAP UI5 developers is on the rise due to the increasing adoption of cloud-based SAP solutions and the need for user-friendly interfaces. By mastering SAP UI5, you can:
- Build innovative SAP applications: Create custom applications tailored to specific business requirements.
- Enhance user experience: Develop intuitive and responsive user interfaces.
- Improve efficiency: Accelerate development processes with pre-built components and tools.
- Expand career opportunities: Increase your job prospects in the SAP ecosystem.
Core Components of SAP UI5
SAP UI5 consists of several essential components:
- SAPUI5 Core: Provides the foundation for building UI5 applications, including basic controls, data binding, and routing.
- SAPUI5 Controls: Offers a rich set of pre-built UI elements like buttons, tables, input fields, and charts.
- SAPUI5 Data Binding: Enables seamless synchronization between data models and UI elements.
- SAPUI5 Routing: Manages navigation within the application.
- SAPUI5 Model: Represents data in a structured format for binding to UI elements.
Getting Started with SAP UI5 Development
To begin your SAP UI5 development journey, follow these steps:
- Set up the development environment: Install Node.js and create a basic project structure.
- Include SAP UI5 libraries: Add necessary libraries to your project.
- Create a basic UI5 application: Build a simple application with basic controls and data binding.
- Explore UI5 controls: Experiment with different UI elements to understand their functionalities.
- Implement data binding: Learn how to bind data to UI elements for dynamic updates.
- Use routing: Create navigation between different views in your application.
- Leverage SAP Fiori design guidelines: Adhere to SAP’s design principles for consistent user experiences.
Building Complex SAP UI5 Applications
As you gain proficiency in SAP UI5, you can tackle more complex projects:
- Integrate with SAP backend systems: Connect your UI5 application to SAP systems using OData services.
- Develop custom controls: Create reusable UI components to enhance productivity.
- Optimize performance: Implement techniques to improve application speed and responsiveness.
- Test and debug: Ensure application quality through thorough testing and debugging.
- Deploy to production: Prepare your application for deployment to different environments.
Best Practices for SAP UI5 Development
To create high-quality SAP UI5 applications, follow these best practices:
- Modularize your code: Break down your application into reusable components.
- Use clear and consistent naming conventions: Improve code readability and maintainability.
- Write clean and well-structured code: Adhere to coding standards for better collaboration.
- Leverage UI5 tooling: Utilize available tools for code completion, debugging, and testing.
- Optimize performance: Focus on efficient data binding and rendering.
- Thorough testing: Conduct unit, integration, and user acceptance testing.
Future Trends in SAP UI5 Development
The SAP UI5 landscape is constantly evolving. Stay updated on the following trends:
- SAP Fiori elements: Utilize pre-built templates for faster development.
- SAPUI5 for React: Explore integration with React for hybrid app development.
- Progressive web apps (PWAs): Build offline-capable and installable UI5 applications.
- UI5 flexibility: Leverage customization options for unique user experiences.
Conclusion
SAP UI5 offers a powerful platform for building engaging and efficient SAP applications. By following the guidance provided in this blog, you can embark on your SAP UI5 development journey with confidence. With dedication and practice, you can become a proficient SAP UI5 developer and create exceptional user experiences.
Tags: SAP UI5, SAP UI5 development, SAPUI5 tutorial, SAPUI5 tutorial for beginners, SAPUI5 training, SAPUI5 course, SAPUI5 online training, SAPUI5 certification, SAPUI5 best practices, SAPUI5 framework, SAPUI5 architecture, SAPUI5 controls, SAPUI5 data binding, SAPUI5 routing, SAPUI5 development tools, SAPUI5 and Fiori, SAPUI5 and OData, SAPUI5 performance optimization, SAPUI5 career opportunities
YOU MAY LIKE THIS
How Managed Services Can Supercharge Your SAP ROI
Why SAP Managed Services Are Essential for Business Growth
SAP Solutions for the Healthcare Sector: Transforming Patient Care
Transforming the Manufacturing Industry with SAP: A Comprehensive Guide