Introduction
Business restructuring, mergers, and acquisitions are all transformative activities that shape an organization’s course. The integration of diverse data systems is one of the major operational obstacles that these methods provide, even while they open up prospects for growth. For smooth operations, well-informed decision-making, and the achievement of strategic objectives, effective data integration is crucial.
Why Data Integration Is Crucial During Transformative Events
1. Unifying Disparate Systems
- Several databases, CRMs, and ERP systems are frequently combined during mergers. Important corporate operations, such as supply chain, finance, and human resources, may run in isolation without integration, which would decrease productivity.
2. Ensuring Business Continuity
- During the transition phase, data integration guarantees continuous workflows and avoids revenue losses.
3. Supporting Strategic Decision-Making
- Executives may evaluate the performance of the recently combined company, find synergies, and make strategic decisions with the use of unified data.
4. Regulatory Compliance
- Following stringent legal and regulatory requirements is frequently a part of business restructuring. Accurate reporting and audit trails are guaranteed by integrated data.
Challenges in Data Integration During Mergers and Restructuring
1. Diverse Data Sources and Formats
- The usage of disparate data systems, formats, and protocols by the participating organizations can make integration more difficult.
2. Data Quality Issues
- Disparate systems often have inconsistent, duplicate, or outdated data, affecting integration outcomes.
3. Security and Privacy Concerns
- To adhere to rules such as the CCPA, GDPR, or industry-specific standards, sensitive data must be safeguarded throughout integration.
4. Limited Resources
- Because mergers and restructurings require a lot of resources, IT teams might not have enough bandwidth to handle intricate data integration initiatives.
5. Cultural and Process Differences
- Integration attempts may be slowed by company cultures and business procedures that are not aligned.
Key Strategies for Data Integration During Mergers and Restructuring
1. Develop a Comprehensive Integration Plan
- Determine which systems are essential and give their integration top priority.
- Establish precise goals, deadlines, and key performance metrics (KPIs).
2. Leverage Middleware and Integration Tools
- Distinct systems can be connected using middleware programs like Boomi, MuleSoft, and SAP Cloud Platform Integration.
3. Conduct a Data Audit
- Evaluate both firms’ data security, relevance, and quality.
- Find inconsistencies, gaps, and duplicates.
4. Standardize Data Formats
- To harmonize datasets, establish consistent nomenclature and data standards.
- To make data transformation easier, use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools.
5. Adopt Real-Time Data Replication
- By ensuring that all systems are using the most recent data, real-time integration helps to avoid delays and discrepancies.
6. Implement Data Governance
- To supervise integration activities, choose data stewards.
- Provide explicit guidelines for the use, access, and retention of data.
7. Utilize AI and Machine Learning
- AI can expedite the integration process by automating data mapping, validation, and deduplication.
Phases of Data Integration During Mergers and Restructuring
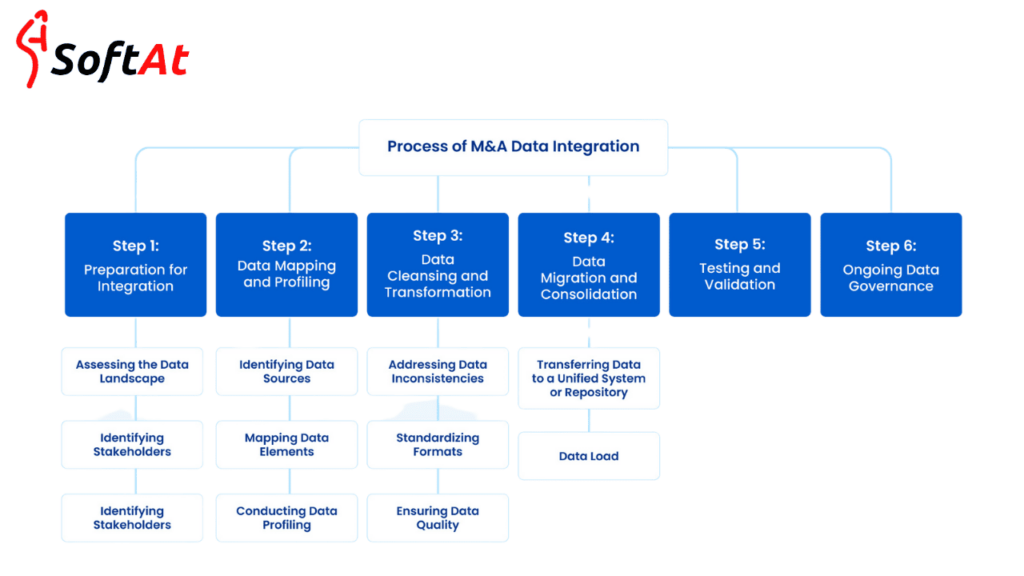
1. Pre-Merger Preparation
- Finding important systems and data sources is known as data discovery.
- Gap Analysis: Draw attention to differences in procedures and data structures.
- Planning: Create an integration roadmap that includes schedules and resource distribution.
2. Integration Execution
- Use scalable and secure tools to migrate data.
- Systems should be synchronized to guarantee continuity throughout the changeover.
- Verify the functionality and accuracy of the data by conducting thorough testing.
- Conduct rigorous testing to validate data accuracy and functionality.
3. Post-Merger Optimization
- Track integration performance and fix problems as soon as they arise.
- Streamline data processes to increase productivity.
- To guarantee adoption, train staff members on the new system.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Data Integration
Case Study 1: Financial Services Merger
- Scenario: To increase their market share, two banking organizations amalgamated.
- Challenge: varied ERP systems with varied data formats were employed by the firms.
- Solution: Financial systems were integrated using a middleware platform, allowing for consistent reporting and compliance.
- Outcome: The combined company improved regulatory compliance and closed month-end transactions more quickly.
Case Study 2: Retail Acquisition
- Scenario: A tiny e-commerce business was purchased by a major retailer.
- Challenge: integrating inventory control systems without interfering with business activities.
- Solution: Inventory data was synchronized across the two platforms through real-time data replication.
- Outcome: Improved inventory accuracy and a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Case Study 3: Business Restructuring in Manufacturing
- Scenario: To cut expenses, a manufacturing company reorganized its supply network.
- Challenge: incorporating information from logistics partners and suppliers into a common ERP system.
- Solution: Real-time supply chain visibility was made possible by API-driven integration.
- Outcome: Cost reductions and increased operational efficiency.
Tools and Technologies for Seamless Integration
1. Data Integration Platforms
- Examples: Automate ETL processes and unify datasets.
- Purpose: Automate ETL processes and unify datasets.
Combine datasets and automate ETL procedures.
2. API Gateways
- Examples: Apigee and Postman are two examples.
- Purpose: Facilitate communication between various systems is the goal.
3. Cloud-Based Integration
- Platforms: AWS Glue with Azure Data Factory.
- Purpose : Expand integration initiatives without spending money on on-premises infrastructure.
4. Data Quality Management Tools
- Examples: IBM Trifacta and InfoSphere.
- Purpose: Data cleansing and validation prior to integration is the goal
5. Machine Learning Algorithms
- Purpose: Automate anomaly detection, deduplication, and data matching.
Best Practices for Data Integration Success
1. Prioritize High-Impact Areas
- Prioritize the integration of vital systems, such as customer data, HR, and finance.
2. Ensure Stakeholder Alignment
- To synchronize goals and expectations, include important stakeholders from both organizations.
3. Maintain Robust Security Measures
- To safeguard sensitive data, use access controls and encrypt data while it’s being transferred.
4. Test Thoroughly
- Do several iterations of testing to find and fix problems prior to launch.
5. Monitor and Optimize
- Analytical tools and dashboards can be used to monitor integration performance and make necessary corrections.
Future Trends in Data Integration
1. AI-Powered Integration
- Complex integration jobs will be progressively automated by AI and machine learning, requiring less human participation.
2. Data Fabric Architecture
- Across hybrid environments, access and integration will be made easier with a single data fabric.
3. Real-Time Edge Computing
- Edge computing will be crucial to real-time data processing and integration as IoT use increases.
4. Blockchain for Data Integrity
- Blockchain technology will give integrated datasets safe, unchangeable records.
Conclusion
- Despite the inherent complexity of corporate restructuring, mergers, and acquisitions, effective data integration techniques can be the difference between success and failure. Organizations can attain a unified, effective, and compliant data landscape by tackling obstacles head-on, utilizing contemporary tools, and adhering to best practices.
- A key component of effective transformation initiatives will continue to be smooth data integration as companies manage ever-changing market conditions.
You may be interested in:
A Deep Dive into SAP API Management
Integration cloud system to HANA Cloud Platform using Cloud Connector