SAP is one of the world’s leading producers of software for the management of business processes.
Founded in 1972, the company was initially called System Analysis Program Development.
The name is an initialism of the company’s original German name: System analyse Programme ntwicklung, which translates to System Analysis Program Development.
helps companies and organizations of all sizes and industries run their businesses profitably, adapt continuously, and grow sustainably.
The company develops software solutions that are used by small businesses, midsize companies, and large corporations. With standard applications, industry solutions, platforms, and technologies, every business process can be mapped and designed. The software collects and processes data on one platform, from raw material purchasing to production and customer satisfaction.
In 1973, the first commercial product was launched. completes its first financial accounting system – RF. This system serves as the cornerstone in the ongoing development of other software modules of the system that will eventually bear the name SAP R/1.
Different Products of SAP:
- ERP and Finance
- S/4HANA Cloud
- ERP for Small and Midsize Enterprises
- Finance
- Accounting and Financial Close
- Treasury Management
- Accounts Receivable, Billing and Revenue Management
- Cybersecurity, Governance, Risk and Compliance
- CRM and Customer Experience
- Customer Data
- Marketing
- Commerce
- Sales
- Service
- Spend Management
- Supplier Management
- Sourcing and Contracts
- Procurement
- Invoices and Payments
- External Workforce and Services
- Travel and Expense
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Planning
- Supply Chain Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Product Lifecycle Management
- Enterprise Asset Management
- Human Capital Management
- Employee Experience Management
- Core HR and Payroll
- Talent Management
- HR Analytics and Workforce Planning
- Business Technology Platform
- Database and Data Management
- Application Development and Integration
- Analytics
- Intelligent Technologies
Specialized Services Provided by SoftAt:
SAP Consulting Services :
S/4 Hana Services
- Integrated Rapid ERP Assessment Services.
- Integrated Implementation Management Services.
- Integrated Application Management Services.
- Integrated Upgrade Management Services.
- Integrated Application Training Services.
- Integrated Custom Application Development Services.
SAP Managed Services :
SAP Basis Support Services
- System monitoring
- performance tuning
- system sizing analysis
- Application Interface management
- Transport management
- User and security management
- Housekeeping jobs/operations
- Backup monitoring
SAP Functional Support
- Day to day operational help desk/end-user
- Troubleshooting
- EDI monitoring and support
- Deployment of new functionalities
- Functional updates / functional enhancements
- Testing of new/enhanced functionalities
- Deployment of new regulations as per statutory requirements
Advanced Managed Services :
SAP ECC Services
- Rapid ERP Assessment Services.
- Implementation Management Services.
- Application Management Services.
- Upgrade Management Services.
- Application Training Services.
- Custom Application Development Services.
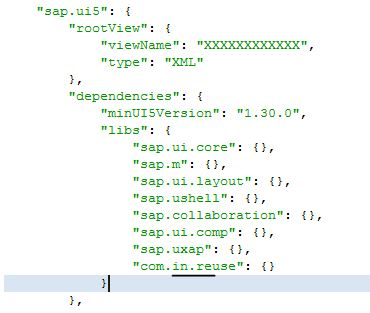
ODATA / FIORI / UI5
- Single sign-on for Fiori
- Enable Offline Functionality
- Custom Fiori client
- Enable RFID, Barcode scanning on Fiori
- Error Handling
- Set up two-factor authorization for Fiori client
- Process Continuity Engine
- Guaranteed Delivery
- High Volume Offline Data Processing
- Offline Authentication
- Offline Attachments
- Data Persistence
- Data sync & Orchestration
- Customer Branding using Fiori
- Conflict Resolution
SAP Development Services :
Application software development service includes:
- Development of a new application platform
- Enhancement / modification / migration of an existing application
- Interfaces to an existing application
- Correction of defects and deficiencies discovered by end-users
- Functionality Extensions
- Functional Help Desk
- Changes to the GUI to make it more user friendly
Implementation services :
- SAP Advanced Deployment
Leverage end-to-end turnkey services to simplify and accelerate your deployment of S/4HANA with services from SAP as your primary partner and project lead.
- Value Assurance
Deploy a systematic approach to accelerate your customer- or partner-led implementation on-premise, in the cloud, or through a hybrid approach with less risk and reduced cost.
- Data Management and Landscape Transformation
Turn data into profit faster by feeding your business applications and processes with the data essential for the digital economy.
- Cloud Professional Services
Use flexible, value-driven expertise to craft a road map, execute the migration, and manage your hybrid or cloud infrastructure securely.
Cloud services :
- SAP Cloud Application Services
Manage, monitor, and improve your SAP solutions investment and processes on any platform with our range of service delivery options and capabilities.
- SAP Cloud Peering
Expand your cloud interconnection ecosystem with the SAP Cloud Peering service and learn about the current state of provider availability.
- SAP Customer Experience Services
Manage every phase of your project, from planning and implementation to operations, confidently with SAP Customer Experience Services.
Unlock the full value of SAP S/4HANA with secure, private, and comprehensive cloud infrastructure and set of managed services.
Build SAP skills and keep them up-to-date with quick access to the latest SAP education content and a vast community of learners.
- SAP Preferred Success
Reduce complexity by accessing resources for fast adoption of cloud solutions, role-based learning, and better incident handling.
MODULES:
Advanced Business Application Programming (ABAP)
ABAP is a programming language that runs in the SAP ABAP runtime environment, created and used by SAP for the development of application programs including:
1. Reports.
2. Module Pool Programming
3. Interfaces
4. Forms
5. Data conversions
6. User Exits & BADI
All of R/3’s applications and even parts of its basic system were developed in ABAP.
ABAP is an event-driven programming language. User actions and system events control the execution of an application.
ABAP is also called ABAP/4. The “4” in ABAP/4 stands for “Fourth Generation Language” or 4GL.
Sales Distribution (SD)
SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) is a core functional module in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that allows organizations to store and manage customer- and product-related data. Organizations use this data to manage all of the sales orders, shipping, billing, and invoicing of their goods and services.
Financial Accounting and Controlling (FICO)
SAP FICO (SAP Finance and SAP Controlling) SAP FICO is an important core functional component in the SAP ERP Central Component that allows an organization to manage all of its financial data. SAP FICO allows an organization to store a complete version of their financial transaction data.
SAP Warehouse Management (WM)
is an important SAP module that provides warehouse management functionality. This module provides tools & processes to maintain inventory at optimum level.
SAP WM course covers all aspects of warehouse management and will provide you with skills to become a successful warehouse manager with complete command over the SAP WM module.
SAP WM is a warehousing management application tool of SAP ERP, which provides critical informational analytical reporting data of warehousing operations like Goods receiving and issuing, batch and quality management in the warehouse, types of movement in the warehouse, etc. which helps in the controlling and management of movement and storage of goods and raw materials within a warehouse with great traceability.
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM)
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) is used to efficiently manage inventory in the Warehouse and for support the processing of goods movement. It allows the company to control their Warehouse inbound and outbound processes and movement of goods in the Warehouse.
The main process in a Warehouse is incoming and outgoing materials, goods receipt and goods issue, fulfilling customer orders, and distribution of goods. When a company doesn’t store any goods, then there is no need of Warehouse management to manage goods.
The inbound process involves the storage of goods in the warehouse and their location and the Outbound process involves picking up the goods. Whenever a material is stored in a warehouse, it is stored in the storage bin and you can find its current location.
Material Management (MM)
SAP MM (Materials Management) is a module in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that provides companies with materials, inventory and warehouse management capabilities. … One of the critical modules in SAP ECC, SAP MM is part of ECC’s logistics function and plays a vital role in a manufacturer’s supply chain.
Production Planning (PP)
SAP Production Planning (PP) is the component of ERP Central Component (ECC) that helps businesses plan the manufacturing, sale and distribution of goods. The master data is used to create transactional data in SAP ECC, such as creating a production order in PP, a sales order in SD, or a purchase order in MM.
Plant Maintenance (PM)
SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) is a component of the ERP Central Component (ECC) that helps businesses support and maintain equipment and systems. Preventive maintenance, which helps to maintain ideal conditions for the system or equipment; and. Repair, for restoring the systems or equipment.
Quality Management (QM)
SAP Quality Management (QM) is a component of SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that helps businesses implement and run quality control processes. It is designed to prevent defects, enable continuous process improvement, and establish sustained quality control programs.
Sales Distribution (SD)
SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) is a core functional module in ERP Central Component (ECC) that allows organizations to store and manage customer- and product-related data. Organizations use this data to manage all of the sales orders, shipping, billing, and invoicing of their goods and services.
Business Intelligence (BI)
Most companies collect a massive volume of business data every day – flowing in from their enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, e-commerce platform, supply chain, and many other internal and external sources. To actually take advantage of this data, and use it to make data-driven decisions, they need a modern business intelligence (BI) system.
BI is sometimes called “descriptive analytics” because it describes how a business is performing today and how it performed in the past. It answers questions like “What happened?” and “What needs to change?” – but it does not get into why something happened or what might happen next.
Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM)
Financial Supply Chain Management is a set of applications from SAP that manages customer-related financial functions such as risk assessment, billing, receivables, and collections, within an SAP ERP environment. Financial Supply Chain Management is designed to increase visibility into and control of cash-related processes between a company and its business partners.
Credit Management – evaluates customers’ creditworthiness using internal and external rating data to facilitate quick credit decisions.
Biller Direct – enables companies to send electronic bills via a link or by attaching a file as an e-mail attachment. The billed customer can then view account information and make payments online.
Collection Management – supports proactive receivables management, including account evaluation and processing of receivables.
Dispute Management – addresses disputes over receivables and provides monitoring that can help detect payment problems early on.
Treasury and Risk Management – provides functions to manage interrelated areas of cash, payments, liquidity, risk, and compliance, along with financial reporting integration.
In-House Cash – processes internal and external payment transactions. It can help to reduce the number of bank accounts a company must hold and the volume of foreign payments that it needs to make.
Logistics Execution (LE)
The SAP Logistics Execution (LE) is used to map the logistical processes of a company. It covers the entire supply chain process – vendor, warehouse, production, distribution & customer. Logistics Execution (LE) comprises of:
1– Inbound process in which goods are collected from the vendor and placed in storage in a warehouse.
2– An outbound process in which the goods are removed from storage and delivered to the end customer.
3– Internal warehouse processes for example posting changes, stock transfers , WM inventory, etc.
4– Transportation process which includes inbound and outbound shipments and the calculation, settlement of shipment costs.
Logistics Execution System (LES) is an integral part of the supply chain. Logistics Execution System (LES) can be integrated into an SAP R/3 System as well as with SAP APO, SAP BW etc.
Project System (PS)
SAP Project System (PS) is a part of SAP’s Project and Portfolio Management solution. Project System helps manage projects throughout the entire project lifecycle, from the creation of a project to the preparation of detailed plans, project execution, and completion.
Due to its tight integration with SAP’s Finance and Logistics modules, the PS Module can be used especially for large and complex projects such as construction, production, service, investment projects in all industries.
One of the strengths of SAP PS as a project management tool is that it can be integrated with other modules as shown in the image below, as well as with external project management tools such as Primavera and Microsoft Project from non-SAP systems.
Companies that start using Project System (PS) gain advantage from subjects below:
1. Organized and detailed follow up of customer and company in-house projects
2. One common platform for project office, logistics units, and finance department
3. Project profitability by phase
4. Resource utilization rates
Human Resources (HR)
The most important objective of master data administration in Human Resources is to enter employee-related data for administrative, time-recording, and payroll purposes.
A new employee can be hired without using Recruitment. Instead you can hire someone by running a personnel action in Personnel Administration, thereby creating the necessary data for the employee to be hired.
Employee data must be kept current. After an employee is hired, circumstances can always arise which necessitate either the entry of new data or the correction of current data. For instance −
- An employee moves to his or her new address must be stored in the system.
- An employee gets a pay hike at the start of the year. The new salary must be stored for the relevant date.
- An employee changes jobs within the organization. His or her organizational assignment, working time, and salary also change.
- Data can be stored for the past, present, or future.
Is SAP good for freshers?
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a widely used enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that is utilized by many organizations across different industries. As a fresher, working with SAP can provide several advantages and opportunities for professional growth. Here are some factors to consider:
- Industry Relevance: SAP is extensively implemented in numerous industries, including manufacturing, retail, finance, healthcare, and logistics. Gaining knowledge and experience with SAP can make you more marketable to employers in these sectors.
- Skill Development: Working with SAP allows freshers to acquire valuable skills related to ERP systems, business processes, and data management. These skills are highly sought after in the job market, and having them can open doors to a variety of career paths.
- Career Opportunities: The demand for professionals with SAP expertise remains high. Organizations require skilled individuals to implement, customize, and maintain SAP systems, as well as provide support and training. Starting your career with SAP knowledge can lead to a wide range of job opportunities and potential for growth.
- Training and Certification: SAP offers training and certification programs that can help you gain a deeper understanding of the software and its modules. These certifications can enhance your credibility and demonstrate your proficiency to potential employers.
- Networking: SAP is a widely used software, and being part of the SAP ecosystem can provide opportunities to connect with professionals and experts in the field. Building a strong network within the SAP community can lead to mentorship, collaboration, and future career prospects.
- Global Reach: SAP is implemented globally, and proficiency in SAP can offer opportunities to work with multinational companies and participate in projects that span across different countries and cultures.
However, it’s important to note that proficiency in SAP alone may not guarantee a successful career. Employers often value a combination of technical skills, domain knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and soft skills. It can be beneficial to complement SAP knowledge with other relevant skills and stay updated with the latest industry trends.
Ultimately, whether SAP is good for freshers depends on individual career goals, interests, and the availability of opportunities in the job market. It’s recommended to research the specific job market in your desired industry, assess the demand for SAP skills, and consider how SAP aligns with your career aspirations before making a decision.