Gamification has turned into a fundamental apparatus across different businesses to upgrade client commitment, support inspiration, and further develop execution. By coordinating game-like components into non-game settings, gamification takes advantage of human way of behaving and brain science, empowering people to partake all the more effectively in undertakings. Whether it’s in schooling, corporate preparation, advertising, or client unwaveringness programs, gamification has demonstrated to be a powerful procedure to connect with clients and advance positive results.
To comprehend the maximum capacity of gamification, it’s urgent to comprehend its execution cycle. The fruitful reception of gamification commonly follows four particular stages, which are intended to draw in clients, guarantee predictable support, and eventually drive conduct change. In this blog, we’ll investigate these four periods of gamification exhaustively, separating how each stage adds to the general adequacy of the gamification methodology.
What is Gamification?
Before we plunge into the stages, we should rapidly characterize what gamification is. Gamification includes applying game-plan components and mechanics — like focuses, levels, identifications, lists of competitors, and prizes — into non-game conditions to expand commitment, inspiration, and interest.
While there’s really no need to focus on transforming everything into a game, gamification utilizes the rules that make games connecting with and applies them to regions like learning, business, wellbeing, and promoting. It’s tied in with making a tomfoolery, intelligent experience that urges members to remain drew in and propelled, frequently through an arrangement of remunerations, difficulties, and social connection.
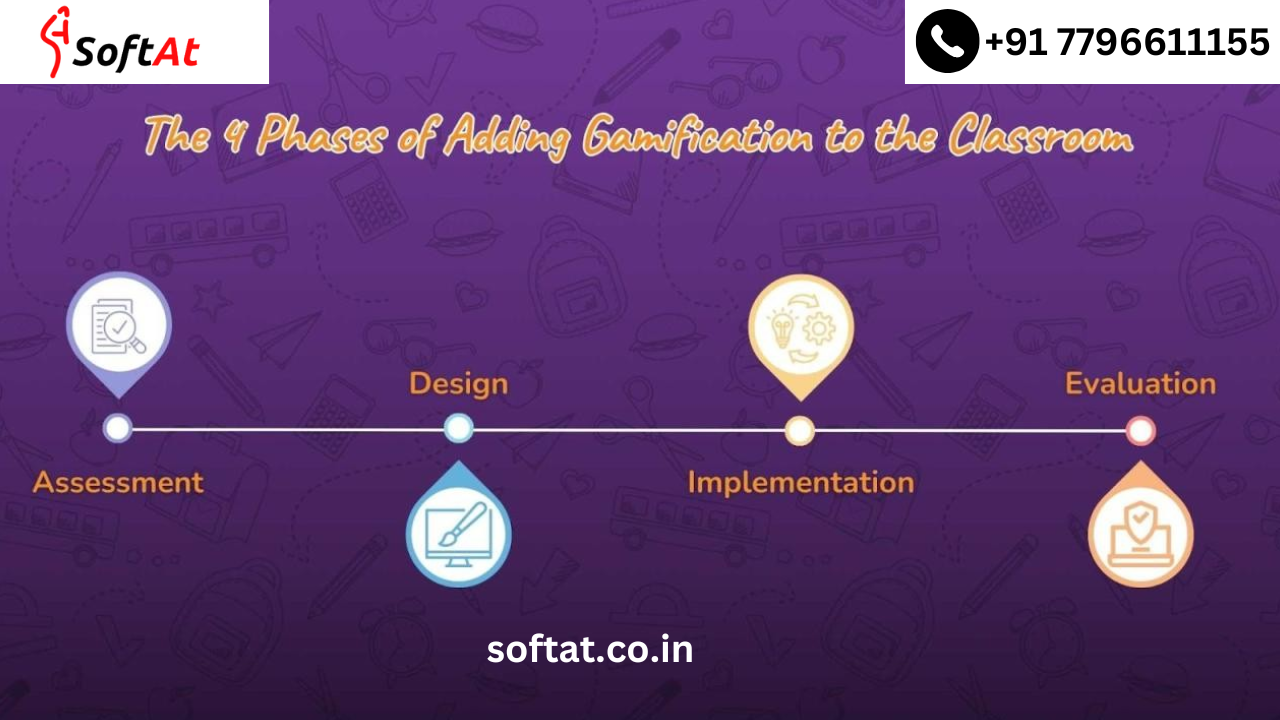
The 4 Phases of Gamification
The method involved with gamifying a movement or framework can be separated into four fundamental stages: Plan, Improvement, Sending, and Advancement. Every one of these stages assumes an imperative part in guaranteeing the progress of a gamified framework. How about we analyze them exhaustively.
Phase 1: Design
The plan stage is where the groundworks of the gamification methodology are spread out. This stage includes cautiously arranging the goals, grasping the crowd, and choosing the right game mechanics to accomplish the ideal results.
- Key Parts of the Plan Stage:
Objective Setting: The most vital phase in planning a gamified framework is characterizing clear, quantifiable objectives. These objectives could be anything from expanding client commitment to upgrading information maintenance, further developing worker execution, or driving client dependability. Without clear goals, estimating the outcome of the gamification effort is unimaginable. - Grasping the Crowd: To plan a gamified experience that resounds with clients, it’s fundamental to comprehend who the interest group and rouses them. Various gatherings might answer better to various sorts of remunerations, difficulties, and levels of contest. For example, more youthful crowds might lean toward competitor lists and moment rewards, while more seasoned crowds could see the value in customized criticism or more cooperative methodologies.
- Choosing Game Mechanics: Game mechanics are the underlying components that drive client conduct in the gamified experience. A few normal game mechanics include:
- Focuses: Used to follow progress and spur clients to accomplish objectives.
Identifications: Address accomplishments and achievements.
Levels: Offer a feeling of movement and prize clients for arriving at higher stages.
Lists of competitors: Empower contest by showing rankings among members.
Challenges/Journeys: Furnish clients with explicit objectives to achieve inside a set time span.
Making a Prize Framework: Prizes are an essential piece of gamification, as they support wanted ways of behaving and results. Prizes can be characteristic (e.g., individual fulfillment) or outward (e.g., substantial awards, acknowledgment). The plan stage ought to distinguish what sorts of remunerations will propel the clients to connect all the more profoundly with the framework. - Narrating and Story: Games frequently recount stories, and integrating story components into a gamified framework can increment client commitment. The story can make a feeling of direction and make the experience more vivid. Whether it’s through characters, difficulties, or objectives, a thoroughly examined story can upgrade the close to home association with the gamified interaction.
Model in real life:
In a worker preparing program, the plan stage could include characterizing the objectives (e.g., further developing information on organization strategies), figuring out representative inspirations (e.g., longing for acknowledgment or progression), choosing the right mechanics (e.g., focuses for finishing modules, identifications for dominance), and making a story around finishing preparing as an excursion of vocation improvement.
Phase 2: Development
When the plan stage is finished, the following stage is to assemble and create the real gamified framework. This stage includes specialized execution and guaranteeing that the game mechanics are incorporated successfully into the client experience.
- Key Parts of the Improvement Stage:
Building the Stage: Whether gamification is being carried out through a current stage (e.g., an eLearning framework, client gateway, or worker application) or through a specially constructed application, the stage should be intended to help the game mechanics. It ought to give an instinctive UI (UI) and smooth route that makes it simple for clients to connect with the gamified components. - Reconciliation with Existing Frameworks: Gamification frequently requires incorporation with other business frameworks, like client relationship the board (CRM), learning the executives frameworks (LMS), or endeavor asset arranging (ERP) frameworks. The improvement stage guarantees that the gamification highlights incorporate flawlessly with these frameworks, taking into consideration the smooth trade of information and a steady client experience.
- Creating Prizes and Acknowledgment Frameworks: The framework for granting focuses, identifications, and levels should be entirely evolved. It ought to have the option to keep tabs on clients’ development, allot rewards in light of explicit activities, and change trouble levels as clients advance. For instance, an eLearning stage could have to create identifications naturally when clients complete specific achievements or levels.
- Client Experience (UX) Plan: The advancement stage likewise incorporates planning a connecting with and charming client experience. This includes guaranteeing that the connection point is easy to understand, the difficulties are suitable regarding trouble, and the prizes are fulfilling to the point of empowering proceeded with interest. Gamification is best when it’s simple and a good time for clients to connect with.
Model in real life:
In a web-based wellness application, the improvement stage would include coordinating the gamification highlights like advancement following, lists of competitors, and difficulties into the stage. It would likewise require fostering a backend framework that tracks clients’ exercises, doles out focuses, and grants identifications for meeting wellness objectives.
Phase 3: Deployment
- Key Parts of the Organization Stage:
Client Onboarding: To guarantee clients comprehend how the gamified framework functions, the sending stage ought to incorporate an onboarding interaction. This could be as instructional exercises, guidelines, or directed walkthroughs to assist clients look into the new highlights, prizes, and objectives. - Showcasing and Advancement: For gamification to find true success, clients should know about it and propelled to partake. Successful advertising and advancement are urgent during the organization stage. For instance, in a client dedication program, organizations could run unique advancements or missions to urge clients to draw in with the gamified framework.
- Input Assortment: At this stage, it means a lot to gather client criticism to comprehend how the framework is being gotten. Criticism can assist with recognizing issues, concerns, and expected upgrades. This criticism can be accumulated through overviews, center gatherings, or direct client communication.
- Screen Framework Execution: During the sending stage, checking the exhibition of the system is basic. Are clients drawing in with the substance? Is it true that they are finishing difficulties? Are there any specialized issues that should be tended to? Checking apparatuses can assist with following cooperation, progress, and specialized usefulness.
Model in real life:
For a recently gamified representative preparation stage, sending would include carrying out the framework to workers, furnishing them with onboarding materials, and sending off a showcasing effort to advance the gamified growth opportunity. Input could be gathered by means of studies to work on future emphasess of the program.
Phase 4: Optimization
The advancement stage centers around further developing the framework in view of client criticism, execution information, and any difficulties experienced during the arrangement stage. Constant improvement is vital to guaranteeing that the gamified framework stays connecting with and powerful over the long run.
- Key Parts of the Enhancement Stage:
Dissecting Client Information: By investigating information on client conduct (e.g., commitment rates, reward finishing rates, input), you can recognize regions where clients might be battling or where the framework can be moved along. This information driven approach takes into consideration more exact acclimations to game mechanics, difficulties, and prizes. - Repeating on Plan: In light of criticism and information, the plan and mechanics of the gamified framework might should be refined. This could include tweaking the trouble of difficulties, presenting new sorts of remunerations, or changing the recurrence of specific undertakings.
- Improving Commitment: After some time, clients might turn out to be less drawn in with the framework assuming it becomes dull. Accordingly, it’s essential to consistently acquaint new components with keep the experience new. This could incorporate adding new difficulties, refreshing lists of competitors, or offering restricted time rewards.
- Long haul Manageability: Streamlining guarantees the gamified framework keeps on conveying esteem over the long haul. This might include extending the program, offering new highlights, or guaranteeing that it adjusts to changing client needs or business targets.
Model in real life:
In a client steadfastness program, enhancement could include examining client cooperation rates and it aren’t quite so engaging as expected to track down that specific prizes. In view of client criticism, the organization could present more important prizes, update the focuses framework, or change the plan to make it seriously captivating.
Conclusion
The 4 phases of gamification—Design, Development, Deployment, and Optimization—work together to create a system that motivates users, enhances engagement, and drives positive behaviors
You may be interested in:
A Deep Dive into SAP API Management
Integration cloud system to HANA Cloud Platform using Cloud Connector