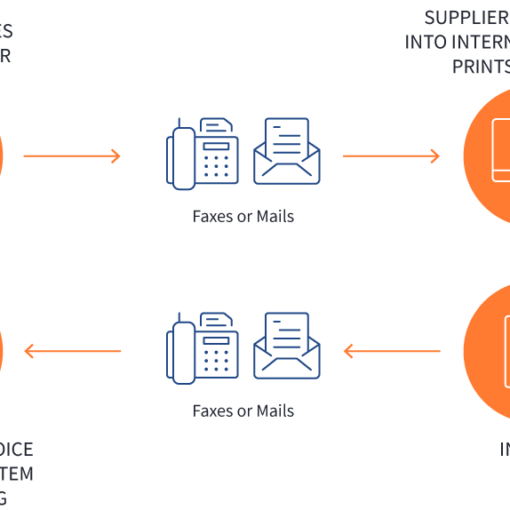
Robotics Process Automation-RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is software technology that’s easy for anyone to use to automate digital tasks. SAP intelligent RPA.
With RPA, software users create software robots, or “bots”, that can learn, mimic, and then execute rules-based business processes. RPA automation enables users to create bots by observing human digital actions. Show your bots what to do, then let them do the work. Robotic Process Automation software bots can interact with any application or system the same way people do—except that RPA bots can operate around the clock, nonstop, much faster and with 100% reliability and precision.
Benefits of RPA?
Robotic process automation streamlines workflows, which makes organizations more profitable, flexible, and responsive. It also increases employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity by removing mundane tasks from their workdays.
RPA is noninvasive and can be rapidly implemented to accelerate digital transformation. And it’s ideal for automating workflows that involve legacy systems that lack APIs, virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs), or database access.
Robotic process automation — or RPA — has been one of the fastest-growing segments in enterprise software because it facilitates the rapid automation of many tasks by simulating the way a human interacts with apps.
SAP intelligent RPA works with the SAP ecosystem to help automate time-consuming processes. Learn what intelligent RPA is, how some companies are using it and a few of its limitations.
SAP intelligent RPA, sometimes referred to as iRPA, is meant to provide better integration into the SAP application stack than other platforms and easier implementation when companies have adopted SAP-prescribed best practices for enterprise processes such as procure-to-pay or quote-to-cash. Organizations can also use intelligent RPA technology as a complement to other RPA platforms that may provide better automation across non-SAP software applications.
Automating best practices
SAP’s current strategy lies in positioning intelligent RPA as a complement to other RPA products and the company is actively partnering with RPA leaders such as UiPath, said Oliver Betz, senior vice president and global head of product management for S/4HANA at SAP. The real strength is pre-building an RPA component into S/4HANA applications, he said. This can help automate the process of creating RPA automations — that is, bots — with less work. SAP launched a program in 2018 to support 10 pre-built automations and now offers about 100.
For example, if a customer is using a standard invoice-to-pay process with standard SAP content, that customer can use an RPA bot out of the box. One of the benefits of this is that these standard processes enforce the best practices observed by SAP from work with the industry in various domains including invoice-to-pay, procurement, sales, professional services and manufacturing.
Automating quickly
The Asia-Pacific office of Rehau, a polymer manufacturer, distributor and designer, recently adopted intelligent RPA.
Intelligent RPA provides deep integration into the organization’s existing SAP backbone, said Chengbo Yu, CIO for the Asia-Pacific region of Rehau. The platform is transparent to business users who are already familiar with SAP. As a result, developing and testing new automations takes less work and requires less of IT’s involvement. RPA projects can move into production in under two weeks, which enables Yu’s team to adopt an agile, iterative approach in improving both the automations and the processes they automate.
Reusing applications
The development tools in intelligent RPA are intended to be well-integrated with SAP applications.
Individual components of the UI are addressable from the studio library and can be dragged into an automation, said Fleming. This makes it easier to use for inexperienced end users trying to automate. It also improves resilience, creating a separation of UI from individual automation projects.
If the target application UI changes. the RPA team can make changes in intelligent RPA in one place without having to manually change each automation that needs to interact with that application.
Embedding intelligence
The design of the SAP Cloud Platform organizes discrete capabilities. so that the individual technologies can work together seamlessly to solve a larger automation problem.
“That creates strength for iRPA because customers are able to do more with the tooling,” Fleming said. For example, intelligent document processing is a layer that most of the RPA vendors are beginning to offer, as they extend capabilities to support AI use cases. SAP has a document processing service, that works with iRPA and is callable by a workflow, a form or by an integration component.
Limitations
SAP intelligent RPA does pose some challenges, however.
Enterprises should keep an eye on the cost to run automations, Bartheidel said. SAP’s licensing model is transaction-based.
Transaction-based licensing requires internal governance and controls to avoid unexpected and unplanned costs,” he said. “On the other hand, it allows a small-budget entry into the world of digital workforce.
Another limitation is that it only works via the cloud. Only being able to access the tools via a browser could limit the potential usage, Bartheidel said. This could be a bigger problem for areas with slow or even no internet connection.
Use Cases:
- Data Entry and Validation: SAP Intelligent RPA can automate the entry of data from various sources into business applications. It can also validate data accuracy by cross-referencing information across systems, reducing the risk of manual errors.
- Invoice Processing: By leveraging computer vision and machine learning, SAP Intelligent RPA can extract data from invoices, validate invoice details, and initiate approval workflows, streamlining the entire invoice processing cycle.
- Customer Service and Support: Bots can assist customer service representatives by fetching relevant information from multiple systems, automating ticket creation, and providing instant responses to common customer queries, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Financial and Accounting Processes: SAP Intelligent RPA can automate financial processes such as accounts payable and receivable, bank reconciliation, and financial reporting, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and faster turnaround times.
Conclusion:
SAP Intelligent RPA is revolutionizing automation by combining the power of RPA with AI technologies. Its seamless integration capabilities, intelligent decision-making, scalability, and enhanced efficiency make it a valuable asset for organizations seeking to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity. By empowering employees and augmenting their capabilities, SAP Intelligent RPA enables businesses to unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, SAP Intelligent RPA is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of automation.